In 2025, AI chatbots are everywhere. Over 987 million people worldwide use them daily, and the global chatbot market sits at a staggering $15.6 billion (projected to hit $46.6 billion by 2029). But most businesses miss a critical point: not all chatbots are created equal.
The chatbots making waves right now? They're self-learning AI chatbots that actually get smarter with every conversation. Unlike those clunky rule-based bots that follow rigid scripts, self-learning chatbots use machine learning and natural language processing to understand context, adapt to user behavior, and continuously improve their responses.
Here's what matters: By the end of this guide, you'll understand how self-learning AI chatbots work, why they're transforming customer service, and how to implement one for your business, even if you're not an AI expert.
What Makes a Chatbot Self Learning?
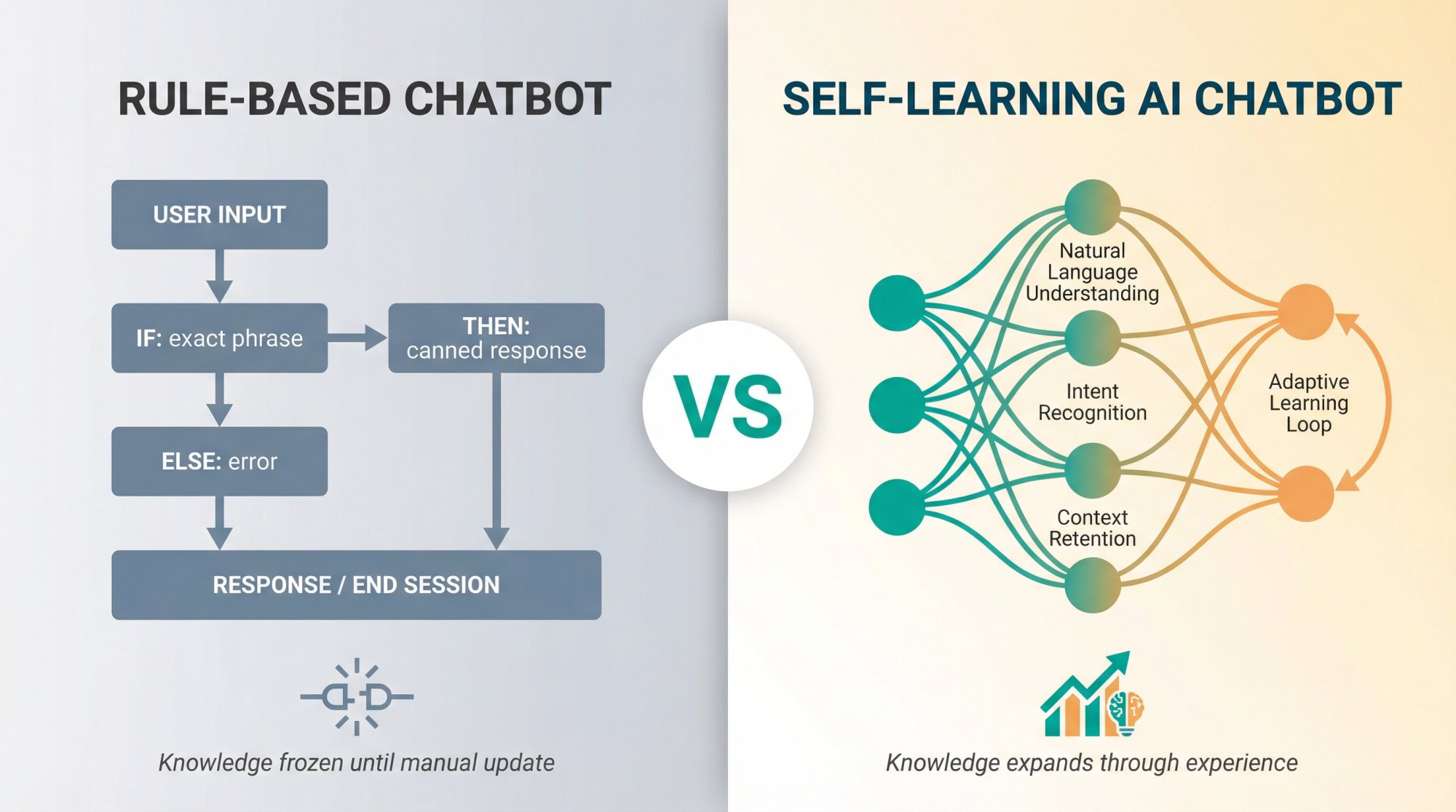
A self-learning AI chatbot is fundamentally different from the bots you probably encountered five years ago. While traditional rule-based chatbots follow fixed if-then scripts (think of them as glorified flowcharts), self-learning bots use machine learning and natural language processing to learn from each interaction and adapt accordingly.
Here's a practical comparison:
Rule-based chatbot: A customer asks "Can I reschedule my Friday delivery?" The bot doesn't understand because it was only programmed to recognize "change delivery date" as an exact phrase. The customer gets frustrated and asks for a human.
Self-learning AI chatbot: The same question comes in. The bot understands the intent (rescheduling a delivery), asks clarifying questions if needed ("Which order are you referring to?"), and either handles it directly or seamlessly connects the customer to your team with full context. Next time someone phrases it differently ("I need to move my shipment to next week"), it handles that too.
Key Characteristics That Set Them Apart
Natural Language Understanding
Self-learning chatbots comprehend free-form text input rather than relying on keyword triggers or button menus. Users can ask questions in their own words, with typos, slang, and all the messiness of real human communication.
Adaptive Learning Loop
The bot learns from each interaction. When it answers a question correctly, it reinforces that knowledge. When it stumbles, it can improve. Over time, it handles variations and even entirely new queries more effectively.
A static bot's knowledge is frozen until a human updates it manually. A self-learning bot's knowledge expands through experience.
Intent Recognition
AI chatbots identify the intent behind questions even when phrased in unfamiliar ways. "I'm flying out tomorrow and need to change my booking" would be understood as a reschedule request. Rule-based bots would likely fail unless that exact wording was pre-programmed.
Context Retention
Many AI bots maintain context over a conversation. Ask a follow-up like "Can you clarify that?" and the bot knows what "that" refers to. Older bots often reset or get confused without explicit context in every message.
Continuous Improvement
Most importantly, a self-learning chatbot doesn't stay static. It uses machine learning algorithms to continuously refine its performance. The more conversations it has, the smarter it gets.
In practical terms, this means conversations feel less like interacting with a vending machine and more like chatting with a knowledgeable assistant who's always learning.
How Do Self Learning Chatbots Work?
Building a chatbot that learns by itself might sound like magic, but it's really a combination of powerful AI techniques and ongoing training. Let's break down what happens under the hood.
Understanding What You Said (Natural Language Processing)
When you send a message to an AI chatbot, the first challenge is comprehending your input. The bot's NLP engine breaks down your text and interprets it.
This involves several sub-steps:
→ Converting the text to a normalized form (lowercasing, removing punctuation)
→ Tokenizing it into words or phrases
→ Using Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to determine your intent (what you're asking for)
→ Extracting relevant entities like dates, product names, or account numbers
Modern AI models excel at this. They don't just look for specific keywords. They actually parse the meaning of sentences. That's why an AI bot can handle "I need to swap my order because the flight is tomorrow" even if it's never seen that exact sentence before.
How AI Chatbots Decide What to Say
Once the bot understands the request, it must decide how to respond. In a self-learning chatbot, this is often handled by an AI-driven dialogue manager or directly by a generative model.
The chatbot can either:
Retrieve a suitable answer from a knowledge base (if it's a Q&A style chatbot with a database of answers)
OR
Generate a response using a language model like GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini
Many enterprise chatbots do both. The bot searches its knowledge base first. If it finds a match, it uses that. If not, a generative AI formulates a new answer in natural language.
Advanced bots also incorporate business logic here: checking user permissions, asking follow-up questions for clarification, or executing actions like placing an order or resetting a password.
The Self Learning Feedback Loop Explained
Here's the secret sauce that makes it truly self-learning. After understanding and responding, the bot doesn't just forget the conversation. It learns from it.
| Learning Mechanism | How It Works | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Retraining on transcripts | Bot periodically retrains ML model on past conversation logs | New examples improve future responses |
| Reinforcement signals | Analyzes user satisfaction cues (rephrasing = missed mark) | Self-corrects based on success/failure |
| Learning new topics | Clusters unknown questions to identify knowledge gaps | Expands topic coverage automatically |
| Human handoff learning | Analyzes what it missed when escalating to agents | Fills training gaps systematically |
Top-tier AI chatbots have a feedback loop that updates their models based on what happened:
Retraining on transcripts: The chatbot periodically retrains its underlying ML model on logs of past conversations. This means all the new examples of questions and correct answers help fine-tune its ability to respond next time.
Reinforcement signals: The bot looks at signals of success or failure. Did the user seem satisfied with the answer or did they rephrase the question (indicating the bot's first answer missed the mark)?
Some systems explicitly ask users "Did this answer your question?" and treat the "Yes/No" as feedback. These reinforcement learning signals help the AI adjust. If many users are unhappy with a certain response, the bot learns to change it.
Learning new topics: When the bot encounters questions on topics it doesn't know, a smart self-learning system flags these. For example, if multiple users ask about a new product that the bot wasn't trained on, the bot can cluster these queries and recognize a gap in its knowledge.
Over time, this means the chatbot expands the range of topics it can handle.
Learning from human handoffs: If your chatbot hands off a conversation to a human agent, some systems learn from that event. The chatbot can later analyze that conversation to understand what it missed and adjust its NLP or add that scenario to its training data.
In practice, continuous learning can be managed through scheduled training updates or even real-time learning. Some platforms retrain the bot's language model overnight on the day's conversations. Others use online learning to update the model on the fly (though this needs careful oversight to avoid learning bad habits from edge cases).
A structured approach works best: Gather a batch of interaction data, have bot trainers review it for correctness, retrain the model with verified data, then deploy the updated model and monitor performance. This ensures the bot improves in a controlled way.
Advanced AI Techniques That Power Modern Chatbots
Modern self-learning chatbots leverage several advanced AI techniques to enhance their capabilities:
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Many chatbots now are built on top of LLMs like OpenAI's GPT series, Google's Gemini, or Anthropic's Claude. These models come pre-trained on billions of sentences, giving the chatbot a base of world knowledge and linguistic ability.
A self-learning bot might use an LLM and then fine-tune it on company-specific data (like your product manuals or FAQs) to specialize it.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
This approach combines search with generative AI. If a user asks something factual like "What's the warranty on product X?", a RAG-enabled bot searches your knowledge base for relevant text and then has the AI model compose an answer using that information.
This way, the chatbot can provide up-to-date and accurate info without needing to have every fact memorized.
Function Calling and API Integrations
Self-learning bots can be augmented to perform actions. Your chatbot might call an API to check a shipping status or book an appointment when asked. This uses a technique where the AI recognizes the user's intent requires an external action ("Where is my order 12345?") and triggers a custom function to retrieve data and return the result to the user.
This turns the chatbot into a true virtual assistant that not only chats but acts.
Multilingual NLP
Self-learning chatbots often have translation capabilities built in. They can detect the user's language and respond in kind, or translate on the fly.
Some platforms use real-time translation APIs so that the bot "sees" the user's message in a default language (say English), processes it, formulates an answer, then translates that answer back to the user's language. This effectively allows one AI model to serve users in many languages.
A note on learning: "Self-learning" doesn't mean the bot becomes an autonomous genius overnight. Most enterprise chatbots learn with humans in the loop supervising the training data that goes in. Truly autonomous real-time learning is trickier due to the risk of errors.
In summary, a self-learning chatbot works through a loop of Understand → Respond → Learn → Improve. It leverages NLP to parse queries, uses AI (and possibly external knowledge) to craft answers, and crucially, it learns from each success or failure to do better next time.
Why Self Learning AI Chatbots Matter for Business
Self-learning AI chatbots aren't just a cool technology demo. They solve real business problems and deliver tangible benefits both to organizations and their customers.
24/7 Instant Support Without Human Limits
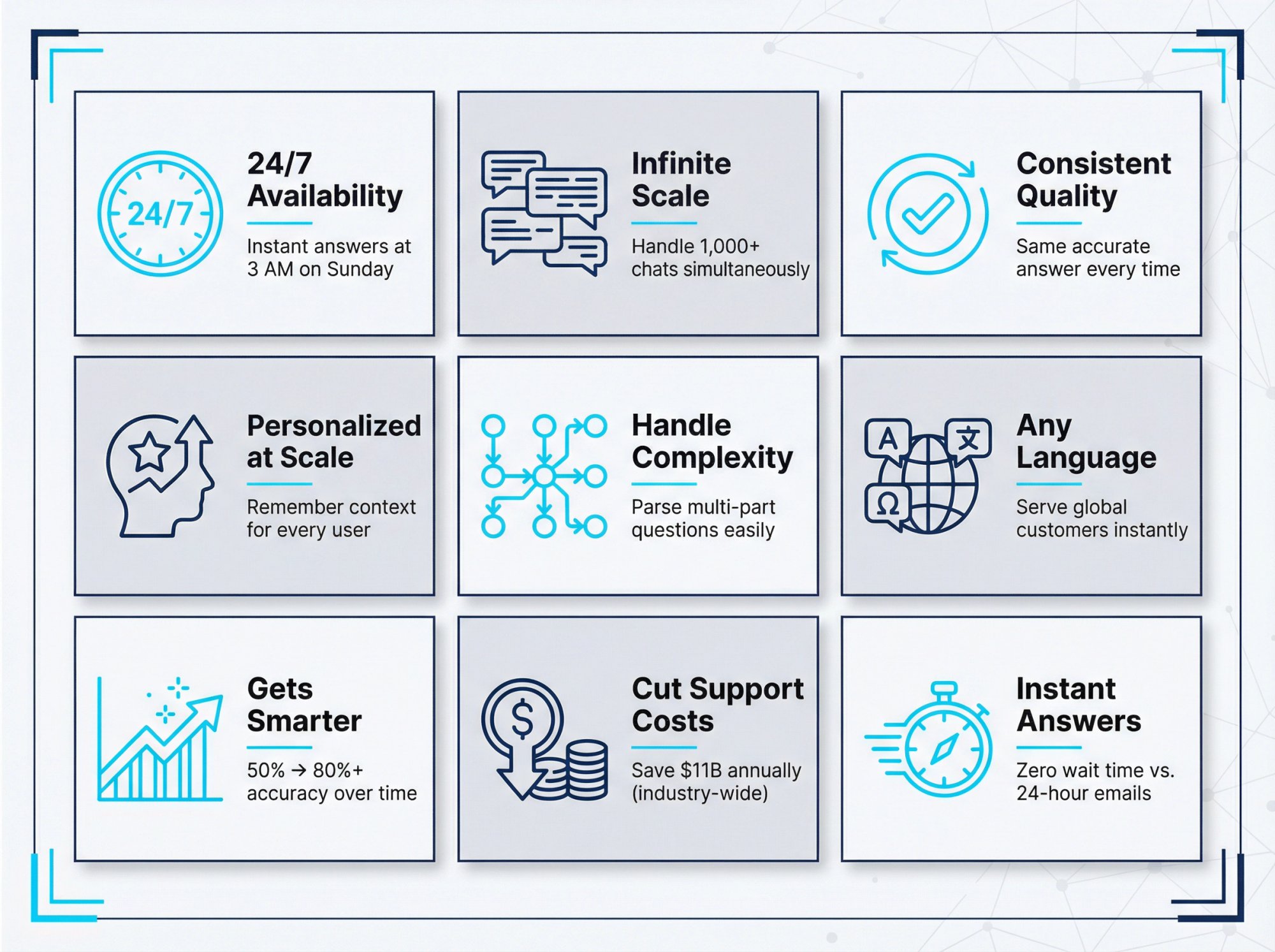
A self-learning chatbot never sleeps. It can handle customer questions at 3 AM on a Sunday just as well as during normal business hours. This round-the-clock availability means customers get immediate answers instead of waiting hours (or days) for an email response.
The result? Higher customer satisfaction and a reputation for responsiveness. Even during holidays or off-hours, your bot is on duty ensuring no inquiry goes unanswered.
Scale Customer Support Without Hiring More Staff
Humans can only handle one conversation at a time. An AI chatbot can handle hundreds or thousands simultaneously. During peak periods or viral campaigns, the chatbot scales effortlessly to meet demand without requiring you to proportionally increase headcount.
If your user queries double next year, the same bot simply works harder. With an all-human team, you'd have to hire and train many new agents to achieve the same.
Deliver Consistent Answers Every Time
Unlike humans who may have bad days or make mistakes, a well-trained chatbot gives consistent answers every time. It reliably provides the correct info (as long as its training is kept up-to-date) and follows defined processes without error.
This consistency improves trust. Customers aren't subject to the luck of which agent they get. A bot won't forget to ask important questions or log a case.
Create Personalized Experiences at Scale
Self-learning chatbots can deliver personalization that's very hard to do manually. Because they remember context and past interactions, they can tailor responses to each user.
For instance, an AI bot can recognize a returning customer and say "Welcome back, Alex! Last time we chatted, you were looking at checking account options. Do you have any more questions on those?"
The bot can leverage CRM data or previous chat history to make the conversation more relevant. Over time, it can even learn user preferences or frequent issues and proactively address them.
Handle Complex Customer Questions Easily
Unlike simple FAQ bots that break when faced with an unexpected question, AI chatbots excel at handling complex or multi-part queries. They use NLP to parse long, detailed customer questions and can ask clarifying questions if needed.
For example, if a user says "My product is making a strange noise and not working properly", a good AI chatbot can handle that by asking follow-ups ("Is it a grinding noise or a high-pitched whine?") and providing troubleshooting steps or guiding the user through a solution.
This kind of conversational adaptability is nearly impossible with rule-based bots that only know predefined flows.
Support Customers in Any Language
Because AI chatbots are language-agnostic (especially if using translation or multilingual training data), they can seamlessly converse in multiple languages. Some enterprise chatbots auto-detect the user's language and respond accordingly.
This opens up your support to global audiences without needing separate bots or teams for each language. One self-learning bot can handle English, Spanish, French, Japanese users all in one system.
Get Smarter Over Time Automatically
This is subtle but perhaps the most important benefit. Because the chatbot gets smarter with use, it delivers increasing returns. The longer you have it deployed and the more interactions it handles, the more valuable it becomes.
Difficult questions that stumped the bot initially get resolved and added to its repertoire. Over a year, your chatbot might go from being able to answer 50% of questions to 80%+ as it learns from new inquiries and edge cases.
A well-optimized self-learning bot doesn't plateau. It keeps learning new solutions, which means your customers' experience keeps improving over time without you having to manually script those improvements.
Cut Support Costs Dramatically
From a business perspective, AI chatbots can drastically cut support costs. By automating answers to common queries, companies reduce the workload on human agents.
Estimates suggest that chatbots could save businesses over $11 billion annually and 2.5 billion hours of work by handling routine conversations that would otherwise require staff.
Instead of needing a large team to answer "Where's my order?" or "How do I reset my password?" 24/7, a single AI chatbot can cover those and escalate only the complex issues to humans. This allows your human support team to focus on high-value interactions while the bot tackles repetitive FAQs.
The outcome? You can scale up your support capacity without linearly scaling headcount or costs.
Answer Customers Faster Than Competitors
Related to customer satisfaction, the speed of answer with a bot is immediate. There's no wait time, hold music, or "your email will be answered in 24 hours."
Immediate answers lead to faster problem resolution. Even when an issue needs a human, the bot often gathers the basic info first (name, account, the issue summary) which saves the agent's time and shortens the overall handle time.
Learn What Customers Really Want
Beyond directly chatting with customers, self-learning bots produce a rich trail of data about what your customers are asking and how those needs change over time.
By analyzing chatbot logs, you can discover common pain points, trending requests, or gaps in your help content. For example, if a question starts popping up often that your bot initially didn't handle, that's a signal of something new customers care about.
In essence, the chatbot not only serves customers but also learns from them and tells you what to improve in your business or content.
Common Self Learning Chatbot Challenges
Before diving into building a self-learning chatbot, it's wise to consider some challenges and how to address them.
Quality of Training Data Matters
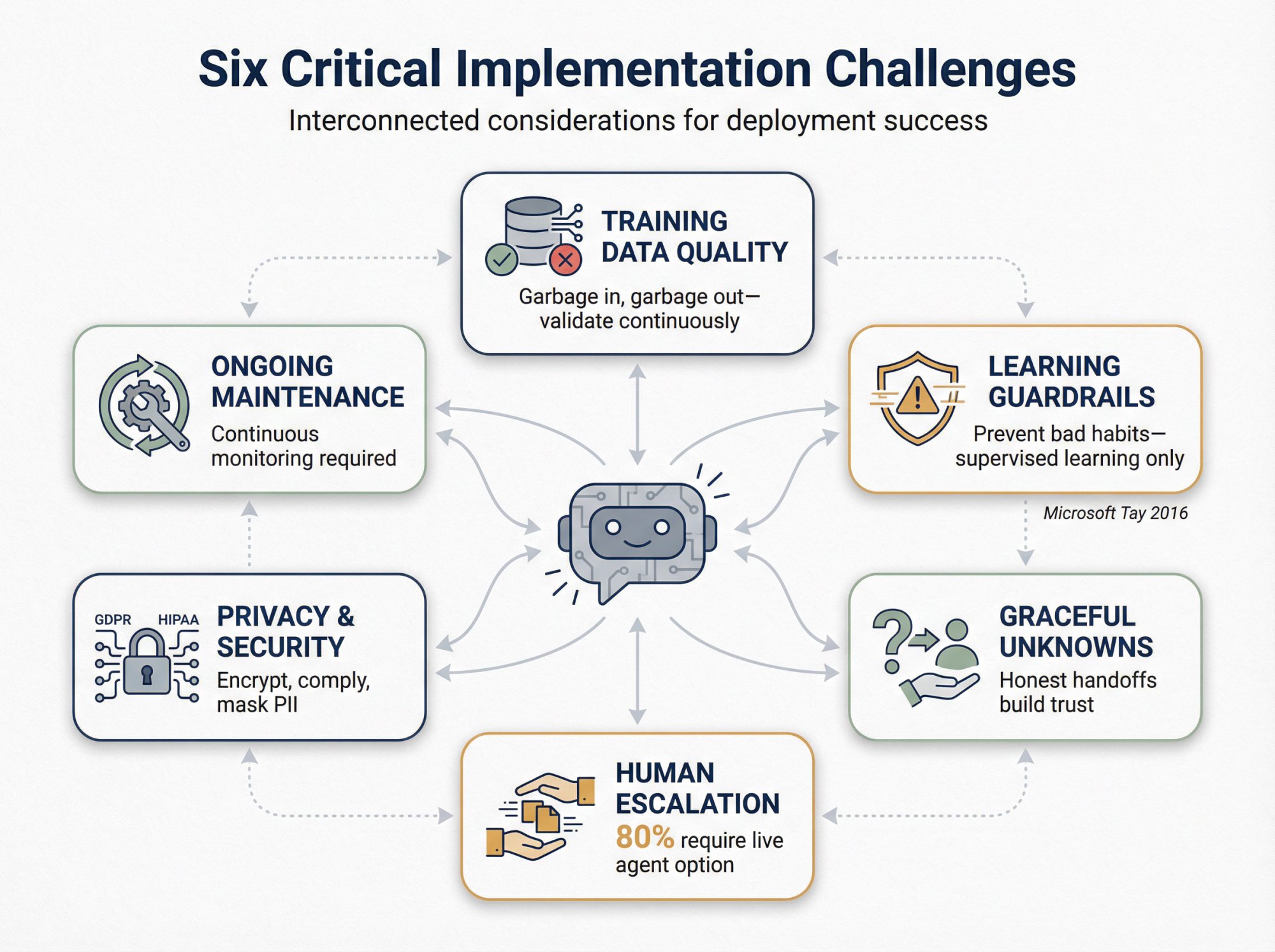
The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" applies to AI chatbots. A self-learning bot is only as good as the data you train it on.
If the knowledge base or FAQs contain inaccurate or outdated info, the bot will happily learn and repeat those errors. Regularly review and update the content the bot uses to formulate answers.
During the continuous learning process, validate what the bot learns. If it's auto-learning from transcripts, have a human check those new Q&A pairs before fully trusting them.
How to Prevent AI Chatbots from Learning Bad Habits
A truly autonomous bot that learns from all user input can go off the rails if not filtered. A notorious example is Microsoft's early experiment "Tay" in 2016, which learned from Twitter interactions and started outputting offensive content after trolls manipulated it.
The lesson? Apply moderation and guardrails. Modern chatbots typically don't blindly learn from user text without supervision. They either learn from approved data or have toxicity filters in place.
Ensure your chatbot platform has safeguards so it doesn't pick up profanity, biases, or confidential info from interactions. Controlled learning (with a human curator in the loop) is often safer for business use than completely unsupervised learning.
What Happens When AI Chatbots Don't Know the Answer
No AI is 100% correct. Your chatbot will inevitably encounter questions it doesn't know or misunderstand some inputs.
How it handles these cases is critical for user satisfaction. The right approach is to gracefully handle unknowns. The bot can say "I'm sorry, I'm not sure about that. Let me connect you with a human agent who can help." and then escalate the chat.
Users appreciate an honest handoff more than a wrong or nonsensical answer. Also, use those failure cases as learning opportunities: feed them into the training data for next time.
Why Human Handoff Is Essential
This is crucial: 80% of people say they'll only use chatbots if they know a live human option is available.
Always provide an easy way for users to reach a human agent from the chatbot (pressing a "talk to human" button or similar). And ensure the handoff is smooth, meaning the human agent receives the conversation context so the user doesn't have to repeat themselves.
Many successful deployments use a hybrid approach: the chatbot answers what it can, and seamlessly summons a human for anything else. This keeps customers happy and confident that they're not stuck in "AI jail" with an unhelpful bot.
The bonus? Through these handoffs, the bot learns its limits and you gather intel on what to train it on next.
Privacy and Data Security Requirements
Chatbots often deal with customer data and potentially sensitive info. It's important to comply with privacy laws and your own data policies.
Make sure users are informed if conversations are recorded for training. Mask or avoid storing personal identifiers in training logs if not needed.
If using third-party AI services (like cloud NLP APIs), understand what data is sent and ensure it's handled securely. If your industry has regulations (like HIPAA in healthcare), ensure the chatbot platform can support compliance.
Always secure the channels. Chats should be encrypted in transit and at rest, and access to bot management should be restricted.
Ongoing Maintenance Is Required
Unlike a static bot that you set and forget, a self-learning bot requires ongoing attention.
You'll want to regularly review its performance: check conversation success rates, review any conversations where users were unhappy or the bot was confused, and update the bot's training accordingly.
Essentially, think of the chatbot as a continuously evolving product. Assign someone to be responsible for its training and quality (sometimes called a bot trainer or conversation designer).
Over time, as the bot gets smarter, the workload will decrease. But it's wise to monitor it continuously, especially after any major changes or new releases of the AI model.
The good news is the bot helps you by surfacing what it's struggling with (through logs and analytics), so you have clear direction on where to improve.
How to Build a Self Learning AI Chatbot
Implementing a self-learning chatbot may sound complex, but modern tools have made it much more approachable. You don't necessarily need a PhD in AI to get started. Here's a roadmap for creating your own self-learning AI chatbot:
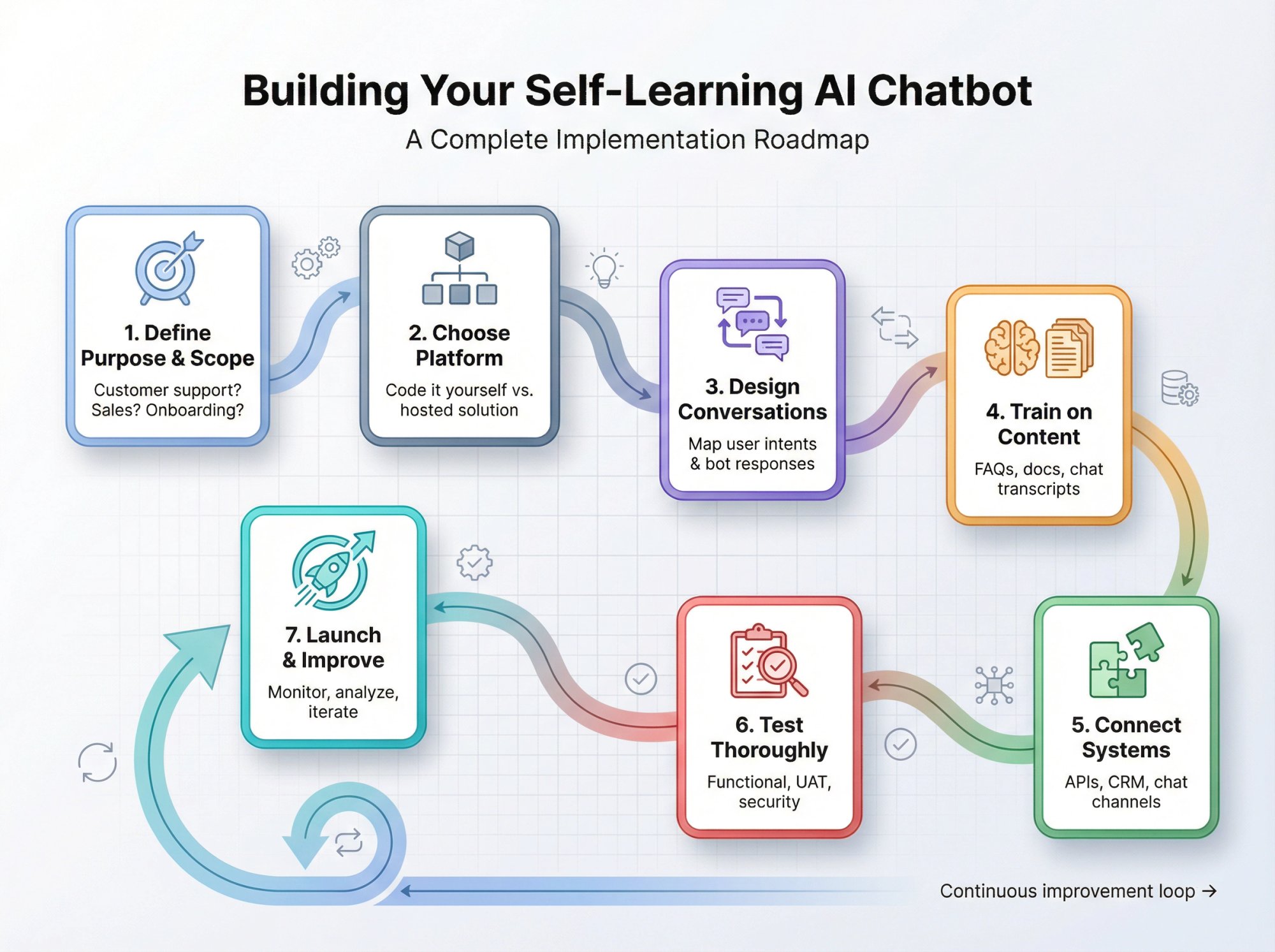
Define What Your Chatbot Should Do
Start by clearly identifying what you want the chatbot to do.
Will this bot handle customer support queries? Aid in sales? Onboard new users? The purpose will guide everything else.
Also define the scope: what topics or tasks should it cover, and what should be left to humans or other systems. For example, you might decide your bot will answer FAQs about your product and provide basic troubleshooting, but anything involving account changes or refunds will go to a human.
Having a well-defined scope prevents "mission creep" and makes training easier.
Choose the Right Chatbot Platform
Next, decide on the technology you'll use to build the bot. There are two broad routes:
Code it yourself using AI libraries (if you have technical expertise). Developers can use Python frameworks with machine learning libraries (like TensorFlow, PyTorch) plus NLP libraries (spaCy, HuggingFace transformers) to build a custom chatbot model. This offers maximum flexibility, but it's complex and time-consuming.
Use a chatbot platform that provides the AI brains and a user-friendly interface. Platforms like Google Dialogflow, Microsoft's Bot Framework, IBM Watson Assistant, Rasa (open source), and others allow you to configure intents, entities, and integrate ML without dealing with algorithms from scratch.
Recently, many new tools have emerged that specifically focus on AI-powered chatbots, including platforms that integrate with GPT or other LLMs.
When choosing a platform, consider factors like:
• Ease of use
• Supported channels (web, mobile, chat apps)
• Integration capabilities
• Language support
• Pricing
• How much control you have over the AI tuning
If your team is non-technical, a hosted platform with a good UI and support might work well. If you have a data science team, you might prefer the flexibility of an open-source framework that you can tweak as needed.
Design How Conversations Should Flow
Even with an AI handling the heavy lifting, you should design how conversations should flow for common scenarios.
Think about the greeting message: how does the bot introduce itself? Then consider the main user intents you expect. For each, outline a happy path conversation.
For example, for a support bot: user asks a question → bot gives answer → user either satisfied or says "that didn't help" → bot then escalates or clarifies.
What if the user asks something ambiguous? Plan prompts for clarifications.
Also decide the bot's tone and persona. Consistency here is key: do you want the bot to be strictly professional or can it use emojis and jokes?
Write sample dialogues to get a feel for the bot's voice. At minimum, define fallback behaviors (like how it responds to off-topic inputs or confusion), and any "don't go there" topics (for instance, telling the bot not to attempt medical or legal advice if that's not appropriate).
Train Your Chatbot on Relevant Content
Now comes the crucial part: giving the bot its knowledge. Gather the training data that covers what the bot needs to know.
This includes:
• FAQs
• Knowledge base articles
• Product documentation
• Chat transcripts from your support team
If you're using a platform like Dialogflow or Watson, you'll be defining intents and uploading example phrases and responses. If you're using a GPT-based approach, you might be feeding documents or a vector database with your content.
The more high-quality, relevant examples you provide, the better the bot will perform. Start with core topics (maybe 80% of common questions) so you get a useful MVP bot, then you can expand.
Also, set the bot's initial fallback prompts. Many platforms allow a list of utterances for things like "I'm sorry, I didn't get that." You want a friendly fallback that doesn't frustrate the user and perhaps invites them to rephrase or offers options.
Connect Your Chatbot to Business Systems
This step is about wiring your chatbot into your environment.
Do you need it to pull data from a CRM or database? For a self-service bot, this might mean connecting APIs (like an order status API, user account API). Many platforms have integration modules or webhooks.
Decide on the channels you'll deploy the bot: your website via a chat widget, messaging apps (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Slack, etc.), or others. Ensure your platform supports those and set up the connections.
If it's on your website, you'll typically add a JavaScript snippet. For other channels, you might need to configure credentials (like linking to your Facebook page or Slack workspace).
Also consider context: if your bot is on a user-authenticated channel, can it know who the user is (greeting them by name because it's in a logged-in area)? Setting up conversation context like user IDs or CRM integration can enable a much more personalized experience.
Test Before Launch
Before unleashing the chatbot on real customers, put it through rigorous testing.
This includes:
Functional testing: Does it correctly understand and respond to sample questions? Try various phrasings of the same question. Does it catch the intent? Test the happy paths and edge cases you mapped out.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Have some beta users or team members interact with the bot as if they were customers. Gather their feedback: was the bot's answer helpful? Did it misinterpret anything? How was the tone?
Performance testing: If you expect high volumes, simulate multiple concurrent users to ensure the bot's infrastructure can handle it. Check the speed of replies. Users will abandon a chat that's too slow.
Security and compliance testing: If the bot handles sensitive info, ensure it's not exposing data. For example, test that it doesn't inadvertently reveal another user's data from an integration.
Fallback/handoff testing: Intentionally ask questions outside its scope. Does it properly escalate to a human or give a useful fallback message? Verify the handoff mechanism works.
During testing, maintain a log of what the bot got wrong or could improve. Update the training data or flows accordingly. It might take a few iterations of training and testing to get the bot to an acceptable success rate.
Don't be discouraged by early mistakes. Learning from those is exactly how the bot gets better.
Launch Gradually and Monitor Performance
When you're ready to go live, consider a phased rollout. You might start with the bot in "beta" on one support page, or live to a small percentage of users, or during certain hours.
This can limit risk as you monitor initial real-world interactions.
Make sure analytics are in place. Track metrics like:
• Number of conversations
• Resolution rate (how often did the bot answer without human help)
• Fallback rate
• User satisfaction (if you have a thumbs-up/down or CSAT survey after chat)
Keep a close eye on the logs when new content or issues pop up. Often, a few days after launch you'll get a batch of real user queries that highlight new things to train the bot on.
Schedule regular reviews (weekly in the beginning) to go over chatbot performance and feed new data into it.
Keep Improving Your Chatbot Over Time
A self-learning chatbot truly shines when you embrace continuous improvement.
Use the closed-loop learning process: collect chat data → analyze failures or new intents → improve training → update the model.
Over weeks and months, this will significantly boost the bot's performance.
Also, update the bot whenever you have new relevant info. If you launch a new product, feed those FAQs to the bot. If policies change, make sure the bot's answers reflect that immediately.
Leverage features like "unknown query" clustering (some platforms automatically group unhandled queries, which you can then answer and add to the bot's knowledge).
Essentially, never consider the bot "done." It's an evolving part of your customer service ecosystem that gets better the more you nurture it.
By following these steps, you'll be well on your way to deploying a high-quality self-learning chatbot. Each step reduces the risk of a disappointing bot launch.
How Social Intents Makes Self Learning Chatbots Easy
At this point, you might be thinking, "This sounds powerful but complicated. Do I need a whole team of AI experts to set this up?"
The good news is no. We built Social Intents specifically to take the technical headache out of building and running self-learning AI chatbots, so even a small team can get started quickly.
Here's how Social Intents can help bring a self-learning chatbot to your website (and other channels) with minimal fuss:
Train AI Chatbots in One Click
Social Intents dramatically simplifies the training phase. Instead of manually compiling and formatting datasets, you can literally point the platform to your existing content and click train.
For example, you can:
• Input your website URLs
• Upload PDFs or docs like user guides
• Import knowledge base articles
The platform automatically ingests that information and uses it to fine-tune a ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini AI model for your chatbot.
In minutes, you'll have a bot that "knows" your company's products, policies, and FAQs. No manual intent mapping or weeks of setup. It's largely automated.
Updating the bot is equally easy. Whenever you have new content or updates, just add the URL or document and re-train with a click. The AI will incorporate the latest info so the bot's knowledge stays current.
Answer Chats in Teams or Slack
One of our unique strengths is how we integrate the chatbot with your team's workflow.
Many chatbot platforms come with yet another dashboard or inbox that your support agents have to monitor. Social Intents instead lets your team answer live chats (when human takeover happens) directly from collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, or Webex.
Essentially, your website's chat widget is connected to a channel in Teams/Slack. When the bot needs to escalate a conversation, your team sees it in the tool they're already using every day. They can jump in seamlessly without switching platforms.
This is a big deal for agent adoption. There's no new interface to learn and no risk of missing chats because it's right in your existing workflow.
Social Intents also provides a web-based live chat console if you prefer, but the key is flexibility. It meets your team where they work.
Seamless AI-to-Human Handoff
As emphasized, smooth escalation to humans is crucial. Social Intents bakes this in.
You can configure when handoff happens (for instance, immediately for certain triggers or only if the user explicitly asks for a human). When handoff occurs, the bot transfers the full conversation context to the agent who takes over (so your team can see what the user and bot have already said).
The platform supports multiple modes:
| Mode | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| AI-only | Bot handles everything | After-hours support |
| Hybrid | Bot answers first, agent can intervene anytime | Most business scenarios |
| Fallback | Bot handles chats only when agents offline/overloaded | Peak periods |
This flexibility means you can tailor the chatbot to your support strategy. Crucially, customers always have a path to a human, which increases trust in using the AI assistant.
Custom AI Actions for Real Business Tasks
Social Intents supports Custom AI Actions that let your chatbot perform tasks and fetch data from other apps.
For example, you can integrate order management so the bot can answer "Where's my order?" by actually querying the order system and returning real-time status.
Or integrate with your ticketing system to log a support ticket when the user says "I want to report an issue."
This moves the bot beyond just Q&A into a true virtual assistant that can handle transactions and personalized requests. It's done by connecting APIs or webhooks. The platform provides templates and guidance for common use cases (order lookups, scheduling with Calendly, CRM updates with HubSpot, Salesforce leads, and Dynamics 365).
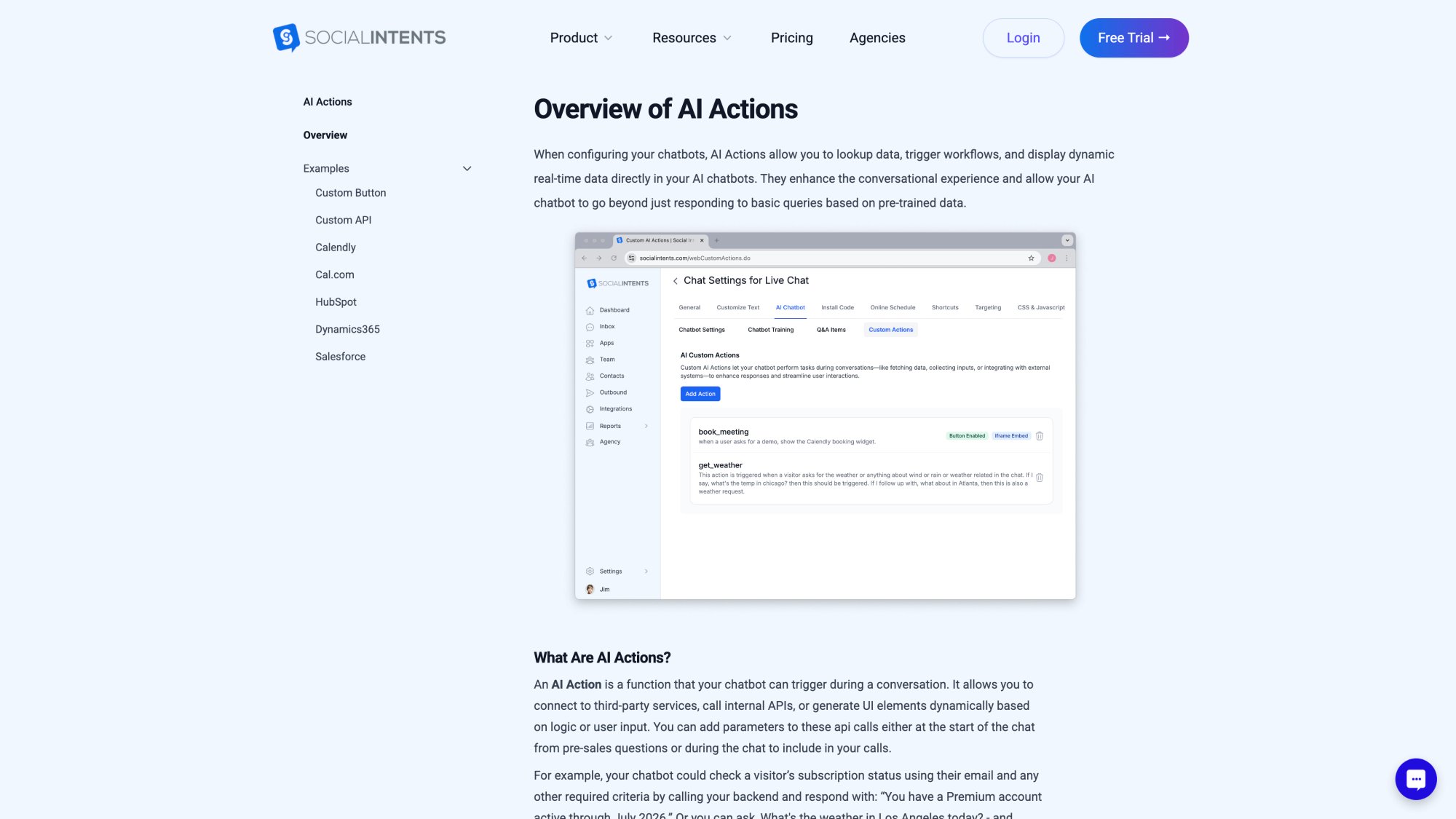
This is a standout feature for businesses that want to offer self-service for account-specific queries securely via the bot.
Deploy Chatbots Anywhere Customers Are
Social Intents allows you to deploy your AI chatbot across multiple channels easily.
You can add it to your website with a few lines of code or via plugins. We have native integrations for:
• Shopify
• Wix
• Webflow
You can also deploy the same chatbot to WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger, which is huge if your customers use those platforms.
Imagine a user can chat with your business's bot over WhatsApp, get instant answers, and if needed, be connected to your team in Slack (all seamlessly). This multi-channel presence means you meet customers where they already are.
Social Intents handles the heavy lifting of each channel's integration. The result? One AI brain, accessible through many avenues.
Built-In Real-Time Translation
If you serve a global audience, Social Intents has you covered with built-in real-time translation.
Using the Google Translate API, the platform can automatically translate user messages and the bot's replies on the fly.
So, a user can type in French, and your English-trained bot will still understand it, find the answer, and reply in French (all in seconds). Each participant sees the conversation in their preferred language.
This allows truly multilingual support without having to train separate bots or manage multiple language datasets. It's a cost-effective way to broaden your support reach globally.
Unlimited Agents on Most Plans
Many chatbot and live chat providers charge per seat (per agent login), which can get expensive as you grow.
Social Intents takes a different approach by offering unlimited agents on most plans (Basic tier and up).
You pay based on features and conversation volume, not by how many team members use it. This is a big advantage if you have a large team or plan to involve many staff in answering chats. You won't be penalized for collaboration.
Even if you only have a few agents now, unlimited means you're future-proofed and can loop in others (like subject matter experts from other departments) without extra cost.
Our pricing is transparent with flat monthly rates for each plan, which is often more predictable than usage-based or seat-based pricing of some competitors.
| Plan | Annual Price | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Starter | $39/mo | 1 widget, 3 agents max, 200 chats/mo, ChatGPT integration, 10 trained URLs |
| Basic | $69/mo | 2 widgets, unlimited agents, 1,000 chats/mo, 25 trained URLs |
| Pro | $99/mo | 5 widgets, unlimited agents, 5,000 chats/mo, remove co-branding, 200 trained URLs |
| Business | $199/mo | 10 widgets, unlimited agents, 10,000 chats/mo, real-time translation, 1,000 trained URLs |
All plans also let you train the AI on a certain number of URLs or documents (with higher tiers supporting more training content), so you can choose based on how much knowledge you need to upload.
White-Label Solution for Agencies
If you're an agency or you want to offer chatbot solutions to your own clients, Social Intents has an Agency/Reseller plan that provides a white-label portal.
This means you can use the platform to create self-learning chatbots for others under your own branding. The agency plan supports multiple sub-accounts and custom branding, so it's like running your own chatbot service powered by Social Intents in the background.
This is particularly useful if you manage websites for clients and want to add value by including an AI chatbot on each site. You get a centralized way to manage all client bots, and clients get access to their bot's dashboard under your label.
Self-learning bots are in high demand. If you're a service provider, this is a path to offer modern AI chat without building it all from scratch.
Real-World Example
Imagine you run an e-commerce store. You can have a ChatGPT-powered bot trained on your product catalog and FAQ up and running on your Shopify site within a day.
It can:
• Answer product questions
• Check order status via a custom action
• Escalate to your support team on Microsoft Teams when needed
All without you writing code or needing AI expertise. That's the kind of streamlined power Social Intents aims to provide.
In essence, we condense a lot of what we've discussed (AI models, training, integration, monitoring) into a user-friendly solution. You don't have to worry about hosting an AI model or dealing with raw model training. We integrate with top AI providers (OpenAI's GPT, Anthropic's Claude, Google's Gemini) under the hood.
You simply provide your content and preferences. The integration with collaboration tools means your team can manage the bot within their daily tools, and features like translation and custom actions are already built-in capabilities to toggle on.
Start your 14-day free trial of Social Intents and see how easy it is to launch a self-learning AI chatbot today.
The Future of Self Learning AI Chatbots
As we look forward, self-learning AI chatbots are poised to become even more powerful and ubiquitous. Here are a few trends shaping the future:
AI Conversations That Feel Human
With rapid advances in large language models (like GPT-4, GPT-5 and beyond), chatbots will continue to close the gap to human-level fluency.
We're already at a point where AI can handle very complex conversations. Future models might master things like emotional understanding and subtler common sense reasoning, making them even more adept at customer service and sales roles.
We may need clearer disclosure that "this is a bot" because it could become hard to tell in casual conversation.
Personalization Based on Individual Users
Chatbots might not only learn in general, but also learn about individual users to personalize service.
Think of an AI that serves as a personal shopping assistant. Over time it remembers your style and preferences so it can proactively suggest items you'd love. Privacy concerns aside, there's potential for chatbots to create very tailored experiences by learning each user's history (with permission).
This could be akin to having an AI concierge who knows you well.
Voice and Multimodal AI Capabilities
We'll see self-learning chatbots moving beyond text. Voice-based AI assistants (Alexa, Google Assistant, etc.) are also getting smarter with self-learning.
In customer service, voicebots on phone IVRs could become as capable as text chatbots. Plus, multimodal AI that can see and interpret images (for example, a customer sends a photo of a defective product and the AI can process that and give instructions) are emerging.
The "chatbot" of the future might handle text, voice, and images seamlessly in one conversation.
Chatbots That Improve Themselves
We discussed the feedback loop involving humans reviewing training. In the future, more of that loop could be automated.
AutoML and continuous learning pipelines might retrain and deploy chatbot models with minimal human oversight, using techniques to ensure safety. Essentially, bots that self-optimize in real-time while minimizing risks.
Industry-Specific AI Chatbots
As the tech matures, we'll likely see more vertical specialization. For example, pre-trained chatbots for healthcare, finance, law, etc., that come with domain knowledge and terminology out-of-the-box.
These can then self-learn further within a company's specific context. Specialized models (e.g., a medical triage chatbot that's been trained on medical texts and can learn from patient interactions) will be more common, accelerating deployment in those fields.
Better AI-Human Collaboration
Rather than AI replacing support agents, the trend is towards collaboration.
We might see AI "co-pilots" for support: the bot might listen into a live chat or call and suggest answers to the human agent in real-time, learning from the agent's choices. Or an agent might oversee a fleet of AI chats, intervening only when needed.
This interplay will get more sophisticated, allowing one human to efficiently supervise many AI interactions at once, maintaining quality with far greater scale.
AI Ethics and Regulations
As AI chatbots become widespread, expect more guidelines and possibly regulations on their use, especially in areas like data privacy, transparency (requiring that users are informed when they're chatting with AI), and accountability (handling scenarios where an AI gives faulty advice).
Companies will need to keep their bots' behavior compliant and ethical. Features like an audit trail of how an AI reached a decision, or manual override controls, will be important in sensitive applications.
Overall, we're moving toward a future where interacting with an AI chatbot is as normal as using a search engine or talking to a smart speaker. Businesses that leverage self-learning chatbots will have a competitive edge in providing instant, intelligent customer service and engaging user experiences.
The key is doing it thoughtfully, using the technology to enhance customer relationships, not replace the human touch entirely.
Common Questions About Self Learning AI Chatbots
What is a self-learning AI chatbot?
A self-learning AI chatbot is a conversational program that uses machine learning and natural language processing to continuously improve its understanding and responses with every interaction. Unlike rule-based chatbots that follow fixed scripts, self-learning bots adapt to new questions, learn from user feedback, and expand their knowledge over time without manual updates to every scenario.
How is a self-learning chatbot different from a regular chatbot?
Regular (rule-based) chatbots follow predefined if-then scripts and can only handle questions they were explicitly programmed to answer. They never learn from new interactions. Self-learning AI chatbots, on the other hand, use NLP to understand natural language, recognize intent even when questions are phrased differently, and improve their responses based on feedback and new data over time.
Do I need coding skills to build a self-learning chatbot?
No. While you can build a custom chatbot if you have programming expertise, modern platforms like Social Intents make it possible to create and deploy self-learning AI chatbots without writing any code. You simply provide your content (website URLs, documents, FAQs), and the platform handles the AI training and integration.
How long does it take to train a self-learning chatbot?
With modern platforms, initial training can take as little as a few minutes to a few hours, depending on how much content you're uploading. For example, Social Intents allows you to point the platform to your website or upload documents, and it automatically trains a ChatGPT or Claude-powered bot on that content. The ongoing "learning" happens continuously as the bot interacts with users.
Can self-learning chatbots handle multiple languages?
Yes. Many self-learning chatbots support multilingual conversations. Some platforms (like Social Intents) use real-time translation APIs to automatically detect the user's language and translate messages on the fly. This allows one bot to serve users in English, Spanish, French, Japanese, and more without separate training for each language.
What happens when the chatbot doesn't know an answer?
A well-designed self-learning chatbot should gracefully handle unknowns. It can say something like "I'm sorry, I'm not sure about that. Let me connect you with a human agent who can help." and then escalate the conversation. The key is providing an easy path to human support (80% of users say they'll only use chatbots if a live human option is available). These "unknown" cases also become learning opportunities for improving the bot.
How much does a self-learning AI chatbot cost?
Costs vary by platform and features. Social Intents offers plans starting at $39/month for smaller implementations, with unlimited agents available starting at $69/month. Pricing typically scales based on conversation volume, number of widgets, and training capacity rather than per-agent fees. Most platforms offer free trials so you can test before committing.
Can self-learning chatbots integrate with my existing tools?
Yes. Modern self-learning chatbot platforms offer extensive integrations. Social Intents, for example, integrates directly with Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, and Webex for agent collaboration. It also connects to e-commerce platforms (Shopify, BigCommerce, Wix, WordPress, Webflow) and can use Custom AI Actions to integrate with your order management systems, CRMs, ticketing systems, and other business tools via APIs.
Are self-learning chatbots secure?
Security depends on the platform and your implementation. Reputable chatbot platforms use encryption for data in transit and at rest, comply with privacy regulations (GDPR, etc.), and offer features like data masking and access controls. When evaluating platforms, check for compliance certifications, data handling policies, and whether they allow you to control where data is stored. If you handle sensitive data (like health information), ensure the platform can meet your specific compliance requirements (such as HIPAA for healthcare).
How accurate are self-learning AI chatbots?
Accuracy improves over time. Initially, a well-trained self-learning chatbot might accurately handle 50-70% of queries. With continuous learning and optimization, many businesses report their bots reaching 80%+ accuracy within months. The key is starting with high-quality training data, regularly reviewing and updating the bot's knowledge, and using the feedback loop to address gaps and errors as they appear.
Conclusion
Self-learning AI chatbots represent a leap forward from the scripted bots of yesterday. They bring together the latest in AI (from natural language understanding to machine learning) to create virtual assistants that truly improve over time.
For businesses, this means the ability to offer scalable, 24/7 support and personalized engagement while controlling costs. For users, it means getting quick, accurate help in a conversational manner that feels intuitive.
Implementing a self-learning chatbot is an investment in both technology and continuous training. But as we've seen, the rewards can be substantial:
• Higher customer satisfaction
• Greater efficiency
• New insights into customer needs
• Major cost savings
• Scalability without proportional headcount increases
Thanks to modern platforms like Social Intents, deploying such a chatbot has never been more accessible. You can tap powerful AI engines like ChatGPT and customize them with your own knowledge base, all without needing to build an AI system from scratch.
The result is a chatbot tailored to your business that keeps getting better with each interaction. A virtual team member who learns on the job, 24 hours a day.
As you consider adding a self-learning AI chatbot to your organization, remember to plan carefully, start with clear objectives, and embrace the iterative learning process. Think of your chatbot not as a one-time IT project, but as a growing, learning part of your customer experience strategy.
Train it, nurture it, and it will reward you with loyal customers and streamlined operations.
In the end, the best customer service is fast, accurate, and available when the customer needs it. Self-learning chatbots, especially when integrated thoughtfully with human support, deliver exactly that. They are quickly moving from a novelty to a necessity in today's digital-first world.
Businesses that get on board now will be well-positioned to delight customers and outpace competitors in the years to come.
Ready to transform your customer experience with a self-learning AI chatbot? Start your free 14-day trial of Social Intents today and see how easy it is to deploy an intelligent chatbot powered by ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini. No credit card required.