In 2025, generative AI has swept through customer service. ChatGPT, OpenAI's large language model, went from being a tech curiosity to something 80% of customer service organizations now use in some form. And it's not hard to see why. Almost every support leader expected that by now, customers would interact with AI-powered bots during their support journey.
ChatGPT offers instant, round-the-clock support at scale. It can handle hundreds of conversations simultaneously and free your human agents to tackle the complex problems that actually need human judgment. But what does "ChatGPT for customer service" really mean in practice? And how do you deploy it without creating more problems than you solve?
This guide covers everything: the concrete benefits you'll actually see, real-world use cases that make sense, how to implement it without needing a team of AI engineers, and the limitations you absolutely need to understand before going live.
Whether you're running a support team trying to cut response times or a business owner exploring AI chatbots for the first time, you'll walk away knowing exactly how ChatGPT can improve your customer service (and how to avoid the common pitfalls that frustrate customers and waste money).
What Is ChatGPT and Why Use It for Customer Support?
ChatGPT is an AI chatbot built on a Large Language Model that generates human-like responses to text prompts. It's trained on massive amounts of internet text, so it can converse, answer questions, write emails, and even generate code. What makes it different from the clunky chatbots you've probably hated in the past is its ability to understand context and nuance in language.
You can ask follow-up questions, clarify what you meant, or request a different tone, and ChatGPT adapts on the fly.
For customer service, this capability changes everything.
Traditional automation meant scripted chatbots or decision-tree phone systems that everyone hates. ChatGPT can engage in actual free-form conversation, addressing a huge variety of queries without needing a pre-written script for each one. It's like cloning your best support rep's knowledge and having them chat with thousands of customers at once, at 2 a.m., on Christmas, in multiple languages.
No wonder 82% of businesses expect AI to disrupt their customer interactions in the next few years.
But ChatGPT itself wasn't built as a customer support tool. It's a general AI that needs to be configured for your specific business and customer-facing use. Used carelessly, it might give irrelevant answers or even incorrect information. The real opportunity comes from integrating ChatGPT into your support workflow through an API or chatbot platform and training it on your company's knowledge.
Forward-thinking teams are already doing this. Nearly 80% of support leaders say AI will play a major role in support's future, especially for handling common queries and improving triage.
ChatGPT for Customer Service: Benefits and ROI
Let's talk about what you actually get when you implement ChatGPT correctly.
How ChatGPT Provides 24/7 Customer Support
Unlike human agents, ChatGPT doesn't sleep or take weekends off. It handles customer questions at any hour, giving immediate answers even at 3 a.m. when your staff is offline. This round-the-clock availability meets modern customer expectations and ensures no visitor leaves your website empty-handed just because it's after hours.
Research shows 64% of people say 24/7 service is the best chatbot feature.
With a ChatGPT-powered chatbot, a late-night visitor can ask about your pricing or return policy and get an instant response, instead of waiting hours (or days) for an email reply. That alone often justifies the investment.
Why ChatGPT Response Times Beat Human Agents
One of the biggest customer complaints? Slow service.
ChatGPT responds in seconds, drastically cutting wait times. It can handle high volumes of inquiries simultaneously, so during peak periods like holidays or product launches, your customers still get prompt help. There's no holding queue. A chatbot can field 100 questions almost as easily as one.
Studies indicate 69% of consumers prefer chatbots for quick replies to simple questions. Faster responses drive higher satisfaction and reduce the load on your live agents.
How ChatGPT Handles FAQs with 79% Accuracy
Support teams answer the same common questions again and again: "What's your shipping policy?", "How do I reset my password?", etc.
ChatGPT excels at these frequently asked questions when properly trained on the answers. It delivers the correct information consistently, without typos or lapses, no matter how many times it's asked. AI chatbots can now resolve up to 79% of routine queries on their own.
By automating repetitive Q&A, you ensure customers always get accurate info and you free your human agents from monotonous tasks.
ChatGPT Multilingual Support Without Hiring Translators
Out of the box, ChatGPT understands and writes dozens of languages. This means you can instantly offer support in Spanish, French, German, Japanese, or whichever languages your customers speak without hiring multilingual staff.
The AI can detect a customer's language and respond accordingly. For global businesses, this is transformative. Everyone gets help in their native language, creating a more personalized experience. Your single AI chatbot essentially becomes a polyglot team of agents.
This capability helps break down language barriers and expand your service to international markets with ease.
How to Scale Customer Support Without Linear Costs
Serving hundreds or thousands of customers one-on-one normally requires an equally large support team. That's expensive.
ChatGPT allows you to scale support without a linear increase in headcount. One AI agent can handle as many chats as needed, so your costs grow much more slowly than your volume. Businesses are finding that automating with AI can save around 30% on customer support costs through efficiency gains.
Research estimates that by automating interactions, companies will save billions of hours and over $8 billion in expenses in 2025 alone.
You can deliver high-quality support to more customers at a fraction of the cost of hiring and training additional staff.
How ChatGPT Improves Agent and Customer Satisfaction
By offloading mundane questions to ChatGPT, your human agents can focus on complex, high-value interactions that truly need their attention.
Agents aren't stuck answering "Is Product X in stock?" for the 50th time. Instead, they tackle tricky technical issues or spend time with VIP customers. This leads to more engaging work and less burnout.
Customers get quick answers to easy questions and more dedicated help on the tough ones. It's a win-win.
Research shows 74% of high-performing service teams are using AI chatbots, and 64% of agents with AI spend more time solving complex problems (versus 50% without AI). The result is higher satisfaction on both sides of the chat window.
ChatGPT for Lead Generation and Sales Support
Customer service isn't just about troubleshooting. It's also an opportunity to engage prospects.
An AI chatbot can proactively greet website visitors and answer product questions, effectively acting as a sales assistant. More importantly, it can capture leads by collecting visitor info for follow-up.
Critical insight: For example, if someone asks about enterprise pricing, the bot can politely ask for their email and then instantly notify your sales team in Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Many companies use ChatGPT bots to qualify leads (identifying serious buyers by their questions) and even upsell or cross-sell products by suggesting relevant items. Because the bot is available the moment a customer shows interest, it can significantly boost conversion rates and capture revenue opportunities that might otherwise be lost after hours.
How ChatGPT Delivers Personalized Experiences at Scale
ChatGPT can deliver personalization that's hard to achieve with templated scripts.
Since it can recall context, an AI agent can reference a customer's previous messages in the conversation, tailoring its responses. With integration to your systems, it could even greet returning users by name and adjust answers based on their account or order history.
For instance, it might say "Hi Jane, welcome back! I see you ordered a Model X last month. Are you asking about accessories for that product?"
ChatGPT can also analyze the tone of a customer's message (whether they sound frustrated or confused) and modulate its replies accordingly. If it detects an angry customer, it might use an extra empathetic tone and immediately flag the conversation for a human to review.
Through AI, even large companies can recreate the feeling of a personal concierge service for every single customer.
These benefits explain why 87% of businesses report AI reduces agent effort and 92% say it saves time resolving issues.
ChatGPT Customer Support Use Cases That Actually Work
ChatGPT can assist customer service in multiple roles. Here are the primary ways organizations are leveraging it today.
1. Automated FAQs and Tier-1 Support
The most popular use case is deploying ChatGPT as a virtual agent on your support channels to handle common questions and requests. This includes:
Answering FAQs:
The chatbot greets visitors and addresses questions about pricing, shipping, return policies, product details, troubleshooting steps, and more. By mining your FAQs and knowledge base, ChatGPT can provide detailed answers and point users to relevant help articles.
Order Status and Tracking:
Customers often ask "Where's my order?" A ChatGPT integration connected to your order database (via an API) can fetch shipping status when given an order number and respond with "Your order #12345 was shipped yesterday and is expected to arrive on Sept 30."
Basic Troubleshooting:
For product support, a ChatGPT bot can walk customers through common troubleshooting steps or how-to instructions. It might provide step-by-step guides on resetting a password or configuring a feature.
Service Information:
The bot supplies info like business hours, plan features, or billing procedures on demand. It's like having a customer manual available 24/7 in conversational format.
This tier-1 support automation has immediate impact. Chatbots can answer 80% of routine questions, leaving only the complicated 20% for human agents. That dramatically cuts down the number of basic tickets flowing to your team.
Thanks to ChatGPT's fluency, customers feel like they're chatting with a helpful rep rather than reading a FAQ page.
2. Agent Assistant and Internal Support Tool
Not every use of ChatGPT is customer-facing. Many support agents are using ChatGPT behind the scenes to boost their productivity. In this mode, ChatGPT is like a real-time coach that helps the human agent rather than talking to the customer directly.
Key applications include:
Drafting Responses:
Agents can paste a customer's question into an internal tool that uses ChatGPT and get a suggested answer. The agent can then review and personalize it before sending. This cuts reply times dramatically while ensuring quality.
Summarizing Tickets:
If a customer writes a long description of an issue, ChatGPT can summarize the main points in a concise blurb. This helps the agent quickly grasp the problem without wading through a wall of text.
Real-Time Data Suggestions:
Some systems integrate ChatGPT to listen as agents chat with customers and suggest relevant info or knowledge base articles in real time. As soon as a customer mentions "refund," the AI might surface the refund policy doc for the agent to reference.
Language Translation:
Agents can leverage ChatGPT's translation ability to communicate with customers in different languages. If an agent only speaks English and gets a query in Spanish, they can have ChatGPT translate it and draft a response.
Knowledge Base Improvement:
ChatGPT can analyze incoming tickets to spot new issues or trends. If multiple customers ask questions your help center doesn't cover, AI can identify that gap. Generative AI can help auto-generate new knowledge base articles when it sees emerging trends.
In these scenarios, ChatGPT acts as a force multiplier for your team. It's not interacting with customers directly (so there's no risk of it saying something inappropriate), but it accelerates the agent's work and helps maintain high quality.
Many companies that are cautious about fully automated chatbots still allow their agents to use ChatGPT internally for these productivity gains.
3. Personalized Recommendations and Upselling
In customer service chats that have a sales aspect (e-commerce, travel bookings, banking), ChatGPT can recommend products or solutions tailored to the customer.
Since it can handle context, an AI chatbot can take into account what it knows about the customer (past purchases, pages viewed, stated preferences) and suggest relevant items or upgrades:
• A customer asks a fashion retailer's bot, "Do you have shoes that match this dress?" The ChatGPT-powered bot analyzes the dress description and recommends specific shoes from the catalog.
• A user tells a telecom support bot, "I'm traveling abroad next week." The bot responds with information on international roaming plans and suggests adding a travel data pack.
• On a SaaS website, a prospective customer says, "I'm not sure which plan is right for me." The chatbot asks a couple of questions about intended usage, then recommends a plan and highlights its relevant features.
These personalized suggestions can drive additional revenue while feeling helpful rather than pushy. Because ChatGPT can incorporate a friendly, conversational tone, customers often respond better to its suggestions than to generic pop-up offers.
4. Sentiment Detection and Priority Routing
Another clever use of AI in support is sentiment analysis, detecting the emotional tone of customer messages. This is extremely useful for prioritization and triage:
Flagging Upset Customers:
If a message comes in like "I am extremely disappointed with your service…" the AI can mark this conversation as high priority so it's addressed immediately by a skilled human agent.
Escalating Urgent Issues:
The AI can route certain sentiments or keywords directly to a human. For example, if someone says "My account was hacked!" the chatbot might bypass normal flows and summon a live agent right away.
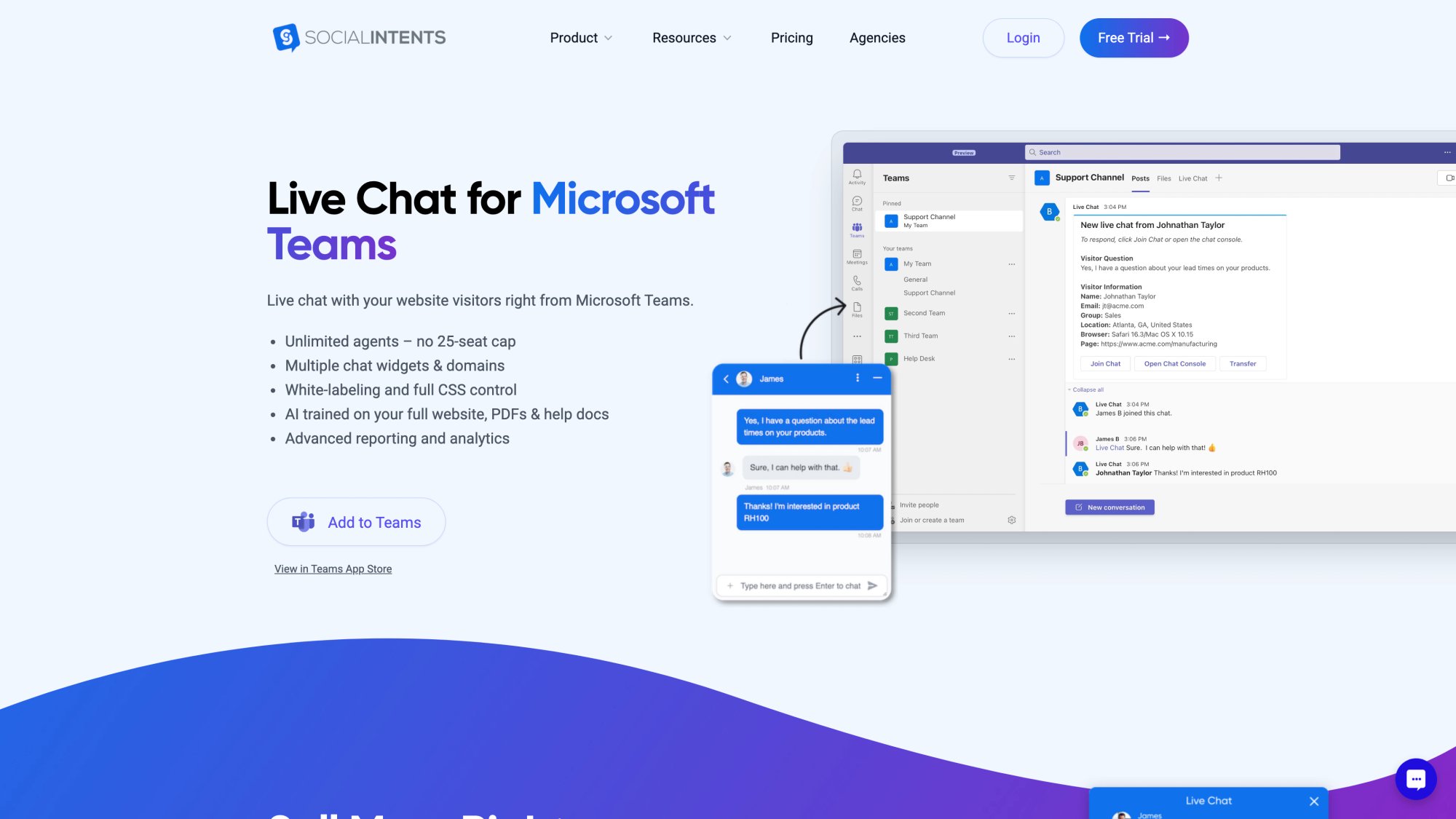
With platforms like Social Intents, you can even set trigger words that automatically bring a human into the chat from Microsoft Teams or Slack.
Queue Prioritization:
Even outside of live chat, AI can triage incoming tickets by sentiment and topic. A polite inquiry about pricing might go in a standard queue, whereas an email threatening legal action would be escalated to a supervisor queue.
Guiding Tone:
For less urgent cases, the bot might just subtly guide the conversation. If it senses frustration, it could switch to a more empathetic tone or offer an apology like "I'm really sorry you're having this issue; let's get it sorted out."
By acting as an emotional radar, ChatGPT helps your support team be more responsive and tactful.
5. Workflow Automation and AI Actions
Beyond chatting, modern AI systems can be wired up to perform actions on behalf of the customer or agent. This uses a concept called function calling or AI actions.
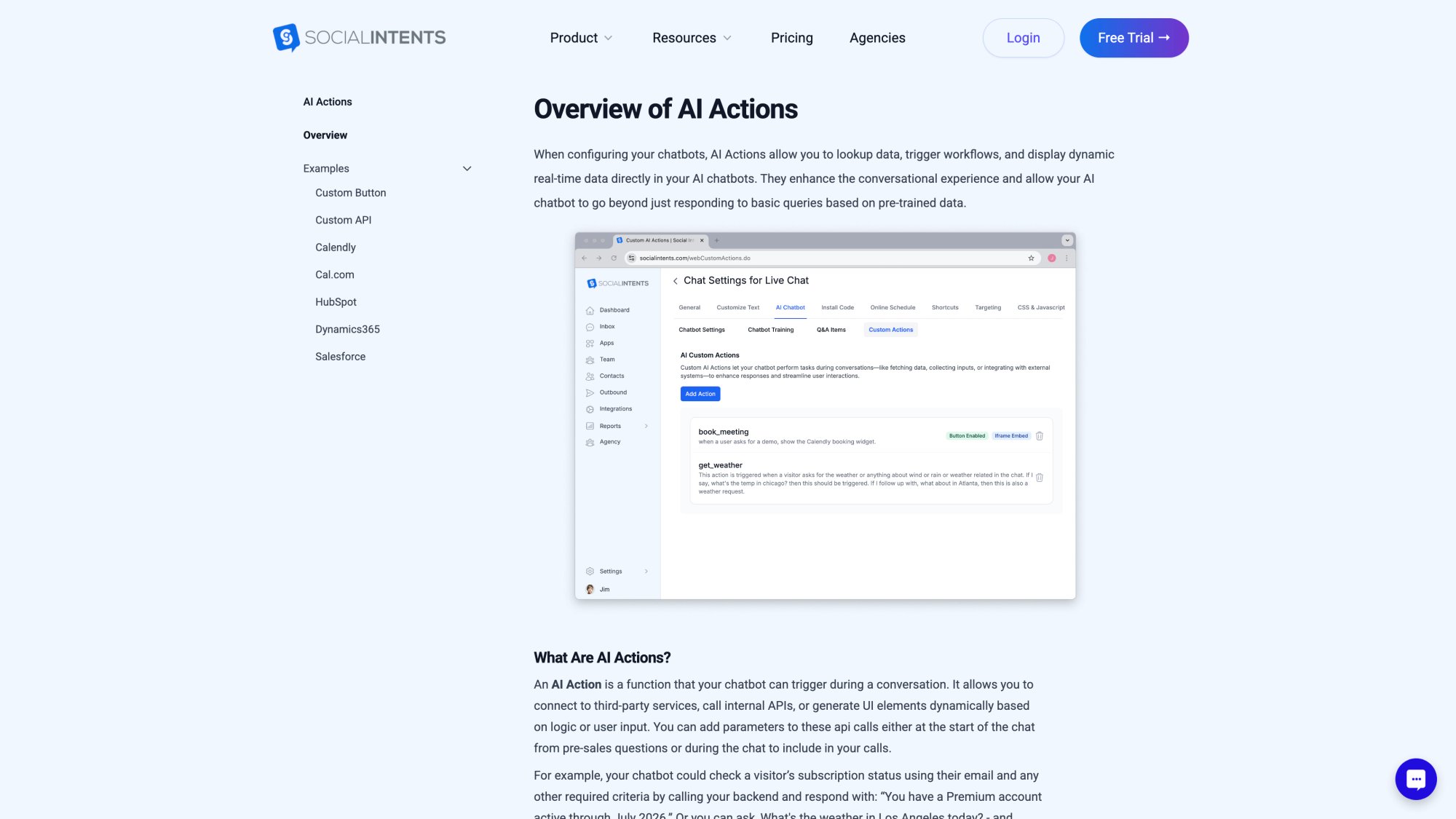
Social Intents' chatbot platform supports custom AI Actions that can look up order info, create helpdesk tickets, schedule appointments, and more. Consider these scenarios:
• A customer tells the bot, "I need to return an item." The ChatGPT bot could automatically create a return merchandise authorization (RMA) ticket in your system and provide shipping instructions, all without an agent touching it.
• Someone says, "I never received my package." The bot could call an "orderStatus(order_id)" function on your back-end. If the result says "in transit, delayed," the bot can relay that and say, "I've flagged this for our team and requested an update from the courier."
• A user asks, "Can I schedule a demo call for tomorrow?" The AI can tap into a scheduling API to offer available time slots and book the meeting.
• The chatbot might even handle simple transactions: "Can you upgrade me to the Premium plan?" The bot calls your billing API to change the plan and confirms to the customer.
This fusion of conversational AI with action-taking transforms the chatbot from a Q&A tool into a true self-service concierge. Customers can accomplish tasks end-to-end through chat, not just get information.
These use cases require integration between ChatGPT and your databases or third-party services, usually via an API. Many customer service platforms (like Social Intents) are building these AI action capabilities in, so non-developers can use them.
How to Implement ChatGPT for Customer Service (2025)
Now for the practical question: How do you actually implement this for your organization?
The good news? It's easier than you think. You don't need a team of AI engineers or a year-long IT project.
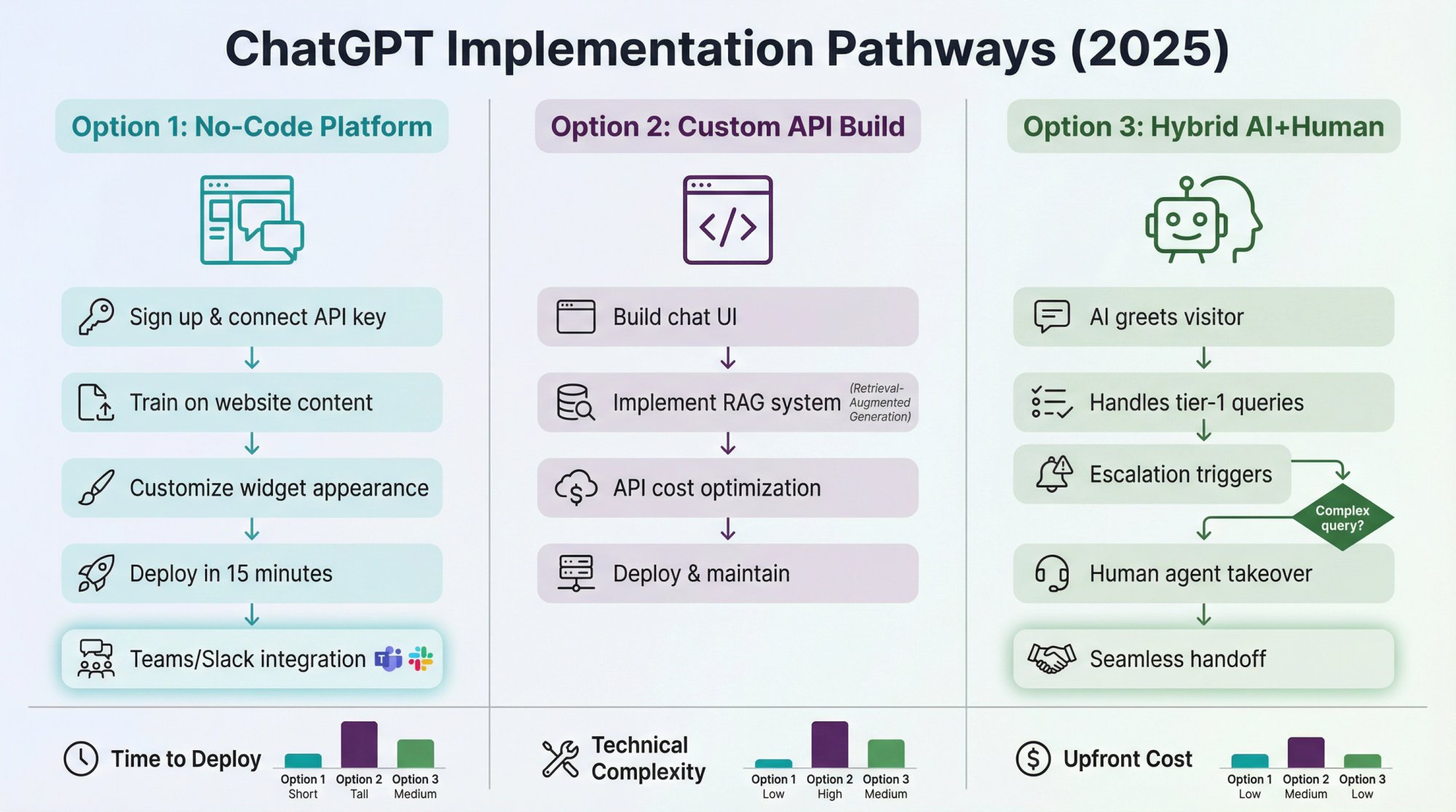
Option 1: Use a Dedicated ChatGPT Chatbot Platform (No Coding)
One of the fastest ways to deploy ChatGPT for support is to use a chatbot platform that offers ChatGPT integration out-of-the-box. These services let you configure an AI-powered chatbot via a friendly dashboard.
You usually just plug in your OpenAI API key (which you can get from OpenAI by creating an account) and tweak some settings. The platform handles all the technical heavy lifting of connecting the AI to a chat interface.
For example, Social Intents is one such platform. It provides a live chat widget for your website that's powered by ChatGPT on the back-end. Setup is straightforward: you sign up, create a chatbot, and paste a snippet of code on your site to embed the chat widget.
You can customize the chatbot's appearance, welcome message, and behavior without any coding.
Crucially, Social Intents integrates with tools like Microsoft Teams and Slack, meaning your human agents can jump into the chatbot conversations from those apps when needed. The AI can be configured to automatically handoff to a human agent in Slack for customer support or Teams for customer support if the user requests it or if certain triggers indicate it's time for a person to step in.
This hybrid approach ensures you get the best of both AI and human support.
When evaluating such platforms, consider:
| Factor | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Ease of Training | How do you teach the bot about your business? Ideally the platform lets you train the AI on your content with one click by pointing it to your website or uploading FAQs. |
| Integration with Workflow | Does it connect with your CRM or team collaboration tools? A big advantage is keeping your team in their normal workflow (e.g., live chats funnel into Microsoft Teams channels where your support team already communicates). |
| Multi-channel Support | Can the platform deploy the AI chatbot to website, mobile app, WhatsApp, Facebook, etc.? |
| Analytics and Control | Good platforms provide dashboards to monitor what customers are asking, how the bot is performing (deflection rate, customer satisfaction), and allow you to fine-tune responses. |
Using a dedicated platform is often best for those who want a quick, relatively hands-off deployment. With Social Intents you can have a ChatGPT-powered bot live on your site in under 15 minutes. Many platforms also offer free trials, so you can experiment without risk.
Option 2: Build with the OpenAI API (Custom Integration)
For companies that have technical resources or unique requirements, using the OpenAI API directly might be the way to go. OpenAI provides API endpoints that let you send a conversation to the model and get a response back.
Building your own integration offers maximum flexibility. You can decide exactly how to handle conversation state, how to route certain queries, and connect the AI to any backend data source or business logic you want.
However, going this route means you need to address some challenges:
User Interface:
You'll need to build the chat interface for customers to interact with (unless integrating into an existing messaging channel).
Conversation Management:
The API gives raw AI responses. You might need to add logic for when to fallback to a human, how to handle clarifications, or how to break a single long answer into chat bubbles.
Knowledge Integration:
By default, ChatGPT's knowledge is limited to its training data. You likely need to implement a retrieval step: when a user asks a question, first search your knowledge base for relevant content and then feed that into the prompt for ChatGPT to use. This is known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), and it ensures the bot's answers are grounded in your real data.
API Costs and Performance:
Using the API costs money per token (though relatively low, often fractions of a cent per query). You'll want to optimize how much text you send and receive to control costs. Also consider latency. Calling the AI takes some seconds, so your system should show a "Typing…" indicator while waiting.
Maintenance:
When you DIY, you're responsible for updating prompts, tweaking parameters, and handling any weird AI behavior.
OpenAI's documentation provides best practices for using the API in customer service contexts. If you have a capable dev team, this approach can result in a very tailored solution that fits into your environment perfectly.
Note: There's also ChatGPT Enterprise (launched in 2023), which is a managed, higher-grade version for businesses with enhanced privacy and data analysis features. And for those concerned about data residency or compliance, Azure OpenAI Service provides OpenAI models through Microsoft's cloud with enterprise-grade security.
Option 3: Hybrid Approach (AI + Live Chat Hand-off)
A highly recommended strategy is the hybrid chatbot approach. This means you deploy ChatGPT alongside your human support team, with clear rules for when the AI should handle things and when it should defer to a person.
In practice, a common hybrid model is:
① Let ChatGPT greet the user and attempt to help initially. The bot can handle the first tier of common issues or questions.
② If the conversation goes beyond the bot's capability (user is unhappy, asks something very account-specific or unusual), then seamlessly transfer the chat to a human agent. The agent can see the chat history, take over, and the customer continues in the same chat window.
③ Optionally, even when the human is engaged, the AI might still work in the background suggesting replies or pulling info for the agent (as an agent assist).
This approach gives you the best of both worlds: efficiency for the easy stuff, and empathy/complex problem solving for the hard stuff.
Importantly, it prevents frustrating the customer. If the AI is confused or the customer insists on a human, the hand-off happens swiftly. Always provide a clear path to a human. Many customers will tolerate a bot as long as they know they can get a human when they want.
From an implementation standpoint, executing a hybrid chat requires that your chatbot is connected to your live chat or ticketing system. Solutions like Social Intents are built with this in mind, so escalating to a human in Microsoft Teams is straightforward.
Hybrid mode can also be time-based. Some companies run the chatbot only outside of business hours (to cover nights and weekends), and during the day, humans do live chat. If the bot can't solve it after hours, it creates a ticket for the team to follow up next day.
This is a smart way to dip your toes into ChatGPT for support. It acts as an after-hours agent that never sleeps, but you still rely on the team during the day. Over time, as confidence in the AI grows, you might expand its duties.
Training and Tuning Your ChatGPT for Success
Regardless of which implementation path you take, one of the most crucial steps is training the AI on your own knowledge and context.
Out-of-the-box, ChatGPT knows a lot (general world knowledge up to its training cutoff), but it doesn't automatically know the details of your company: your product specs, your policies, your terminology. You have to feed it that information or give it a way to look it up.
Here are key methods to ensure your ChatGPT deployment is knowledgeable and accurate:
Knowledge Base Ingestion:
Gather your FAQs, help center articles, product documentation, and provide them to the AI. Many chatbot platforms allow you to upload documents or point the bot to your website to "crawl" your content and train itself.
They index that data so when a user asks something, the bot can fetch a relevant snippet and include it in the prompt to ChatGPT. If doing this custom, you might use a vector database to store embeddings of your texts and retrieve the most relevant ones for each query.
Define Your Tone and Guidelines:
You can give the AI a persona or style guideline via its prompt. For example: "You are an empathetic customer support assistant for a luxury retail brand. Always address the customer by name and use a warm, friendly tone. If the customer is upset, apologize and reassure them you will fix the issue."
This helps the AI maintain consistency and match your brand voice. Many platforms have a field where you can input such instructions for the bot.
Set Boundaries:
Tell the AI what not to do. For instance: "Do not answer questions that ask for legal or medical advice. Do not reveal internal company information. If you aren't confident in an answer, politely say you will forward the request to a human agent."
Setting these rules can prevent the AI from going off-script or providing unsuitable responses.
Use Examples (Few-Shot Learning):
Provide a few example Q&A pairs in the prompt. For instance: "User: How do I reset my password? Agent: Sure! Click 'Forgot Password' on the login page, then check your email for a reset link…"
A couple of these examples can teach the AI the style of answers you like.
Continuous Learning:
Treat your AI assistant as a living project. Monitor the chats. Review where the bot did well and where it stumbled. If it gave a wrong or subpar answer, update your knowledge base or add that question to the training data with the correct answer.
Over time, this iterative tuning makes the bot more reliable. Also, incorporate feedback from your human agents: if they notice the bot often struggles with a certain topic, take that as a training opportunity.
Confidence Thresholds:
Some setups allow you to adjust a confidence level. If the AI's internal confidence in its answer is below a threshold, you can have it not answer and instead say "Let me connect you with a human" immediately. This avoids the bot confidently delivering incorrect information when it's not sure.
Testing:
Before deploying at full scale, test the chatbot with real-world scenarios. Create a list of common questions and some oddball ones, and see how it handles them. Also test edge cases like users typing gibberish, or being rude, to ensure the bot's responses are appropriate.
Many companies do a soft launch where the chatbot is offered to a small percentage of users initially, and then ramp up once it proves itself.
By thoroughly training and configuring ChatGPT for your environment, you transform it from a general AI into a domain expert AI. This step often marks the difference between a mediocre chatbot and a stellar one that customers praise.
ChatGPT Customer Service Best Practices (2025)
Implementing ChatGPT in customer service involves rethinking some processes and keeping a close eye on quality and customer experience.

Be Transparent It's AI:
It's usually wise to let customers know they're chatting with an AI (at least initially). Many companies will have the chatbot introduce itself with a name like "Hi, I'm Alex, the virtual assistant. I can help with many questions or connect you with a human if needed!"
This transparency sets proper expectations. Most customers don't mind a bot for quick answers. Research shows 67% of customers globally used a chatbot for support in the past year. But they appreciate knowing upfront.
Hiding the fact that it's AI can lead to distrust if the user figures it out later.
Always Offer a Human Option:
Make it easy for customers to break out of the bot flow. If a user types things like "human" or "agent" or expresses frustration, the bot should respond with an apology and escalate them.
Even a simple persistent menu like "Chat with human agent" can be provided in the UI. The goal is excellent support, not forcing AI for AI's sake. Human backup is your safety net.
Monitor Conversations Regularly:
Don't "set and forget" your chatbot. At least in the early stages, have someone review a sample of interactions every day or week.
This helps catch any weird answers or unhappy customers that the bot didn't handle well. Look for patterns: are there questions it doesn't answer correctly? Is it taking too many turns to resolve simple queries?
These insights will guide improvements.
Educate and Involve Your Support Team:
Your human agents should not see ChatGPT as a threat, but rather as a helper. Involve them in the rollout. Explain how the bot works, what it will handle, and how it will escalate issues to them.
Encourage agents to give feedback on bot performance. Some team members might even enjoy being the "bot manager" who trains and fine-tunes the AI.
Also, train them on how to seamlessly take over from the bot without making the customer repeat themselves (e.g., reading the chat transcript before saying hello). When the team is bought in, the human-AI collaboration becomes very powerful.
Define Metrics of Success:
Determine how you'll measure the impact of ChatGPT on your service. Common metrics include:
• Resolution Rate: What percentage of conversations does the bot resolve without human intervention?
• Deflection Rate: How many chats/tickets are avoided from humans thanks to the bot.
• Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Ask users to rate the chatbot interaction. Monitor this relative to your normal CSAT.
• First Response Time & Average Handle Time: These usually improve with a bot; quantify it.
• Agent Productivity: Are human agents able to handle more cases or focus on harder issues?
• Cost Savings: Compare support costs (or workload) before vs after.
By tracking these, you can objectively see the value and know where to adjust.
Address Data Security and Privacy:
When integrating AI like ChatGPT, remember that any customer data you send to it (chat transcripts, personal info) is potentially sensitive.
Make sure you're using a solution that complies with your privacy requirements. OpenAI's policy (as of 2023) is that they don't use API data to train their models and you can request retention controls, but you should still avoid sending unnecessary personal data in prompts.
If you handle health or financial data, consult your compliance team. For extra-sensitive cases, consider hosting AI in a controlled environment (like Azure OpenAI or on-prem solutions if available).
Start Small and Expand:
You don't have to automate everything on day one. A prudent strategy is to start with a limited scope: deploy the bot for just one use case or one segment, like handling only FAQ inquiries on your website's help page.
See how it performs and gather feedback. Then gradually expand its knowledge and audience. This phased approach limits risk and lets you iron out kinks in a controlled way.
Plan for Continuous Improvement:
AI customer service is an evolving domain. New model versions will emerge (GPT-4, GPT-5, etc.), and features like better context handling or plugin integrations are continuously being developed.
Stay informed on updates from your AI or platform provider. You might need to retrain or update your bot as the models improve. Also, keep feeding it fresh data: if you launch a new product, make sure the bot gets the new FAQs; if your policies change, update those in its knowledge base promptly.
An outdated bot can be more harmful than no bot.
Manage User Expectations in UI:
Design the chat experience thoughtfully. Simple things like showing typing indicators ("AI is typing…") help manage expectation so users don't feel the bot has frozen.
If the AI needs to call an external API that might take a few seconds (like checking a database), consider having it send a quick message like "Let me check that for you…" to avoid dead air.
End the conversation gracefully too, with "Glad I could help! Have a great day!" or if no solution: "I'm sorry I couldn't resolve this. I'll escalate to a human colleague now."
Following these best practices will help ensure your venture into AI support is successful and well-received by customers and agents alike.
ChatGPT Limitations: What to Know Before You Deploy
As powerful as ChatGPT is, it's not a magic fix for everything. Implementing it blindly could cause problems. Here are key challenges to be aware of (and how to mitigate them).

1. Hallucinations (Incorrect Answers)
ChatGPT has a known flaw: it can sometimes produce answers that sound confident but are completely incorrect.
This happens because the model tries to predict a plausible answer, and if your knowledge base doesn't cover the question well, it might guess or even make something up. In customer service, a hallucinated answer could mean giving a customer bad info (an incorrect refund policy or a nonexistent feature description). This can be worse than not answering at all.
Mitigation: Always ground the AI in your actual data. Use retrieval augmentation so it cites the real policy text when answering policy questions. Set up fallback rules: if the AI's confidence is low or it doesn't find supporting info, it should either prompt the user for clarification or escalate, rather than inventing an answer.
Regularly review logs for any incorrect answers and add those cases to the training data.
2. Lack of True Understanding
ChatGPT is not truly intelligent in a human sense. It doesn't "understand" the world or your business goals, it just predicts text based on patterns.
So it might miss nuances or context that a human would catch. For instance, if a user says "I'm not happy with your product," a human agent might infer this is a potential cancellation risk and respond with a retention approach. The AI might just offer generic troubleshooting, missing the bigger picture.
Mitigation: Provide the AI with as much context as possible (e.g., customer history) and explicitly instruct it on situations like this ("if customer expresses dissatisfaction, offer to make it right or involve support manager").
Also accept that some level of human oversight is needed for truly nuanced situations. High-empathy, sensitive cases (serious complaints or emotional topics) might be best left to humans.
3. Security and Privacy Concerns
Sending customer data to an AI service raises privacy issues. There's also the risk that the AI might inadvertently reveal something it shouldn't.
For example, if not properly constrained, an AI integrated with your database could expose another user's data due to a prompt injection attack (where a malicious user types input that tricks the AI into ignoring its instructions).
Mitigation: Work with IT/security teams on a data policy. Mask or avoid sending personally identifiable information (PII) in prompts whenever possible (for instance, use a customer ID instead of full name).
Leverage built-in content filters that OpenAI provides to avoid toxic or sensitive outputs. If using third-party platforms, review their security measures and data processing agreements.
For industries like healthcare or finance, consider private deployments or ensure the vendor will sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) if needed for HIPAA compliance.
4. Inability to Handle Edge Cases
There will inevitably be questions the AI can't answer (either because they are very product-specific, or it's something genuinely new that it hasn't been trained on).
Also, ChatGPT's knowledge (unless it has browsing enabled via a plugin) might be outdated on some topics beyond its training cutoff.
Mitigation: Maintain a mechanism for unknowns. The bot should be able to say, "I'm not sure about that, let me connect you to a specialist." It's better to admit not knowing than to mislead.
Also, continually update the AI's knowledge as new products launch, new issues arise, etc. Treat it as a knowledge management exercise, which benefits your whole support team, not just the AI.
5. Brand Voice and Tone
If not configured, the AI's tone might be overly verbose or too casual/formal for your brand. We've all seen ChatGPT give somewhat lengthy, super-polite answers that might feel off in a quick customer chat context.
Mitigation: Tweak the prompt to enforce your desired tone. If your brand is young and fun, you might allow emojis and a light-hearted style. If your brand is formal, you instruct the AI to be succinct and professional.
Review transcripts for tone. If it sounds like a "robot" or too generic, inject more of your brand personality. The advantage of ChatGPT is it can really embody a style if you train it.
6. Customer Acceptance
Not every customer will embrace a chatbot. Some may be impatient and immediately demand a human, or they might not trust the answers given by an AI. Also, accessibility could be an issue: for some elderly or non-tech-savvy customers, dealing with a bot can be confusing.
Mitigation: Provide alternative channels prominently. Still offer a phone number or an email option on your support page, in case someone really doesn't want to chat with a bot.
Make sure the bot's responses are clear and helpful to build trust. Perhaps even cite knowledge sources (some bots say "According to our policy page, …").
And if a customer asks the bot directly "Are you a robot?", instruct it to answer honestly and helpfully ("Yes, I'm an AI assistant, but I'm here to help you with any questions. If I can't handle it, I'll get a human for you.").
7. Over-Reliance on AI
There's a strategic risk in leaning too heavily on AI and potentially underinvesting in your human team or other support avenues.
ChatGPT is amazing, but it's not a panacea for all support challenges. Complex problem-solving, building long-term customer relationships, gathering nuanced customer feedback (these still need humans).
Mitigation: Use AI to augment, not replace, the human touch. Free up your people's time to do the higher-level work: creating proactive support content, improving product based on support insights, or giving VIP customers white-glove treatment.
Keep an eye on satisfaction metrics; if you see them dip after implementing AI, investigate if maybe the pendulum swung too far and you need to dial back or adjust where AI is used.
When aware of these limitations, you can plan around them. Many early missteps with AI in customer service happened when companies deployed bots without understanding these challenges, resulting in public fails or customer ire.
By acknowledging what ChatGPT can and can't do, and setting it up with guardrails, you can avoid the pitfalls.
Will ChatGPT Replace Customer Service Agents?
This question comes up a lot: if ChatGPT can do so much, will it eventually replace human customer service agents entirely?
The short answer in 2025: No, but it will certainly change their role.
ChatGPT and similar AI are extremely good at certain tasks: answering straightforward questions, providing information, and even handling some transactions. They can do this faster and cheaper than a human in many cases.
However, there are areas where humans still have the upper hand:
Emotional Empathy:
Humans genuinely understand what another human is feeling and can adjust in nuanced ways. In a delicate situation (a customer is really angry or visibly distressed), a human agent's ability to listen, apologize sincerely, and build rapport is hard for an AI to match.
Complex Problem Solving:
If an issue requires reading between the lines, making judgment calls, or creatively troubleshooting when the solution isn't known, humans excel. AI can only work with what it's seen before or logical extensions of that. Truly novel problems will stump it.
A human agent can gather info, form a hypothesis, test a solution (essentially, think). There's also accountability; a human can take ownership: "I will personally make sure this gets fixed for you," which carries weight.
Personal Connection:
Especially in B2B or high-end consumer contexts, clients may expect a relationship with a dedicated account manager or support engineer. The reassurance of having John from Company X who knows your case is something an AI avatar can't fully replace.
Strategic Insight:
Human support agents often do more than answer queries. They gather feedback, sense market trends, upsell in a nuanced way, and can act as the voice of the customer internally. AI can gather data but not interpret the business implications as well.
What we're likely to see is a shift towards a blended AI+Human model as the new normal. AI will handle, say, 50% of interactions end-to-end (maybe more for simple consumer businesses, less for complex B2B). Humans will handle the rest, but those will be the higher-impact interactions.
So the human role might become more specialized: they'll be experts who step in for the thorny issues, or they'll be managing the AI to ensure it's doing its job correctly. In essence, support agents may evolve into AI supervisors/trainers and relationship managers, rather than password-resetters and copy-pasters.
The net effect could be positive for agents: their work becomes more engaging as the drudgery is offloaded. But it does mean skill requirements will change. Agents will need to be adept at using AI tools, interpreting AI outputs, and focusing on advanced soft skills.
From the customer perspective, they will increasingly encounter AI as a first point of contact. If done well, they won't mind as long as their issue is resolved.
People didn't used to like automated phone systems because they were clunky; but with AI chat that works well, a lot of customers actually prefer it for speed and convenience. Research shows usage of ChatGPT-like tools among Americans roughly doubled from 2023 to 2025, indicating growing comfort with AI assistance.
So the foreseeable future is AI and humans working hand-in-hand. Think of AI as the first-line support and the humans as second-line and escalation.
As experts note, a combination of AI and human customer service is likely to become the norm, with AI handling simpler queries and humans stepping in when necessary.
We are already seeing that play out. Rather than "AI replacing agents," it's more accurate to say "AI is elevating the role of agents" and filtering how their time is used.
How to Get Started with ChatGPT for Customer Support
If you're convinced ChatGPT can improve your customer service, here's how to move forward:
① Start with a pilot.
Pick one use case (maybe FAQ automation on your website) and test it on a small scale. Get feedback, refine it, and gradually expand.
② Choose your implementation path.
For most teams, a no-code platform like Social Intents is the fastest route. You can have a ChatGPT bot live in under 15 minutes, and it integrates with your existing workflow in Teams or Slack.
③ Train the AI thoroughly.
Feed it your FAQs, policies, and product docs. Set clear boundaries about what it should and shouldn't answer. Test it with real scenarios before going live.
④ Involve your team.
Get your support agents bought in. They can help train the bot and provide feedback. Make sure they understand this is a tool to help them, not replace them.
⑤ Monitor and iterate.
Review conversations regularly. Track your metrics (resolution rate, CSAT, deflection rate). Keep refining the bot based on what you learn.
⑥ Scale gradually.
As confidence grows, expand the bot's knowledge and give it more responsibilities. Maybe start with just your website, then add WhatsApp, then Facebook Messenger.
The companies that succeed will be those that leverage AI tools to deliver service that's not only more efficient, but also more human-feeling in the ways that count. Speed and scale from AI, empathy and creativity from people (together, that's a recipe for truly outstanding customer service).
ChatGPT for Customer Service FAQs
Is ChatGPT accurate enough for customer service?
ChatGPT can be highly accurate when properly trained on your company's knowledge base. However, it can sometimes "hallucinate" or provide incorrect information if not properly configured. The key is to ground the AI in your actual data through retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and set up confidence thresholds so it escalates to humans when uncertain.
How much does it cost to implement ChatGPT for customer service?
Costs vary widely depending on your approach. Using OpenAI's API directly costs fractions of a cent per interaction. No-code platforms like Social Intents typically charge monthly subscription fees (often $50-$200/month depending on volume and features). Most businesses save around 30% on customer support costs overall despite the implementation costs.
Will customers be frustrated talking to a bot instead of a human?
Not if implemented thoughtfully. Research shows 69% of consumers prefer chatbots for quick replies to simple questions. The key is to be transparent that it's AI, always offer an easy path to a human agent, and ensure the bot actually resolves issues rather than creating more frustration.
How long does it take to set up ChatGPT for customer service?
With a no-code platform, you can have a basic ChatGPT bot live in under 15 minutes. However, properly training it on your knowledge base, testing it thoroughly, and refining it based on feedback typically takes 2-4 weeks for a production-ready deployment. Custom API integrations can take several months.
Can ChatGPT handle multiple languages?
Yes, ChatGPT supports dozens of languages out of the box. It can detect a customer's language and respond accordingly, making it excellent for global businesses. You can offer multilingual support without hiring multilingual staff.
What happens when ChatGPT can't answer a question?
A properly configured ChatGPT bot should recognize when it doesn't have the information needed and either ask clarifying questions or escalate to a human agent. Platforms like Social Intents allow you to set trigger words that automatically bring a human into the chat from Teams or Slack.
Is ChatGPT secure enough for customer data?
OpenAI doesn't use API data to train their models, and you can request retention controls. However, you should avoid sending unnecessary personal information in prompts. For highly regulated industries (healthcare, finance), consider private deployments through Azure OpenAI Service or ensure your vendor will sign appropriate compliance agreements (BAA for HIPAA, etc.).
Can ChatGPT integrate with my existing helpdesk software?
Yes, ChatGPT can integrate with most major helpdesk and CRM platforms through APIs or pre-built integrations. Platforms like Social Intents offer native integrations with Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, and Webex, allowing your team to handle AI-escalated conversations in tools they already use.
Will ChatGPT replace my customer service team?
No. ChatGPT excels at handling routine queries and providing information quickly, but humans are still essential for complex problem-solving, emotional empathy, and building customer relationships. The future is a hybrid model where AI handles simpler queries and humans step in when necessary. Your team's role will evolve to focus on higher-value interactions.
How do I measure the success of ChatGPT in customer service?
Track these key metrics: resolution rate (percentage of conversations the bot resolves without human help), deflection rate (how many tickets are avoided), customer satisfaction (CSAT scores for bot interactions), first response time, average handle time, and cost savings. Research shows 87% of businesses report AI reduces agent effort and 92% say it saves time resolving issues.
What's the biggest mistake companies make with ChatGPT for customer service?
The biggest mistake is deploying ChatGPT without proper training on company-specific knowledge and without clear escalation paths to humans. This leads to incorrect answers, frustrated customers, and poor adoption. Always train the AI thoroughly on your FAQs and policies, set clear boundaries for what it should and shouldn't handle, and make it easy for customers to reach a human when needed.


