Are you wondering how to increase student engagement on your campus? Looking for some solid strategies to engage college students?
Did you know: Only 60% of all those who started college actually earned a degree within six years in 2017. The numbers are even worse for Black students (39.9%) and Hispanic students (54.4%).
Student completion is in crisis mode, and it needs some serious effort on the part of higher-ed institutions to turn it around.
But why are students dropping out? The biggest culprit is engagement in its many forms, and we will discuss all those in detail in this article. In a nutshell, disengaged students hide learning difficulties or even giftedness. They may become unmotivated in one or all topics, lack focus, and curiosity, and eventually become a problem for teachers also.
So, how can student engagement solve all this and more? This is what I am going to talk about in this article and give you practical strategies that you can apply for increasing student engagement.
Let us jump right in!
Main reasons why students drop out
Wrong course enrollment
Unprepared high school students who do not properly understand the undertakings of particular course content, enroll for it. Or students who lack study skills for a particular course enroll for it and later find it hard to go through with it.
Difficulty navigating systems
The stress of the enrollment process itself, like the selection of colleges, application, and admissions process takes a toll on students’ ability to make the right choice in terms of a college degree.
Personal non-academic barriers
Health issues, financial problems, mental health struggles, child care challenges, transportation difficulties, and a sense of disconnect from the college community.
High tuition fee
Especially true for economically weaker sections of students where the receipt of any grant aid increases the probability of student persistence and degree completion. But it is equally applicable to other classes also, as most families and students are relying on loans to help pay the high tuition fees, and currently owe a combined $1.7 trillion for their education
Online and non-traditional student challenges
Non-traditional are adult learners, student parents, veterans, first-generation students, and basically, anyone who doesn’t look like your typical 18- to 22-year-old on campus.
So, for example, a working mom who is also a student doesn’t get access to the same resources that everyone else does. She has both work and family commitments and trying to complete a degree at the same time.
Also, if an online student is watching a classroom video, he doesn’t get the opportunity to then ask a professor a question. For example, if he is thinking about changing his major, who does he speak to about it?
There are a lot of services that are available on campus that are lacking in the online world.
A one-size-fits-all student experience
As I mentioned earlier, the college dropout for black and Hispanic students is much higher than average. So, an important area to address is the student experience itself.
According to a 2019 study, Black, Hispanic, and first-generation students report a lower sense of belonging at four-year schools (but not at two-year schools)
Lack of support
‘I quit simply because it was boring!’, or ‘I quit because no one cared if I drop out’. These are also some reasons why students give up on higher education – directly related to lack of engagement.
Sometimes students are simply unhappy with college and are going through a discouraging environment at college with nagging roommates, overload of course material, etc., and decide to give up.
So how can student engagement help overcome these reasons? Let us get to it.
How increasing student engagement helps turn this around?
Higher engagement improves student motivation
While non-college-related factors also influence levels of motivation in students, there are many issues affecting student motivation in the classroom. And often these college-related demotivating factors contribute to disengaged behaviors.
The good thing is that because these are college-related, you can do everything to change them and turn them into motivating factors.
Colleges can use both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation tactics to improve engagement in the classroom and beyond. We will take about these in detail in our strategies section.
Engaged students are good students
No teacher wants crickets in their class, which is a high possibility if you have disengaged students in your class. And the problem may keep getting worse if one or many of the following factors are also present:
- Lack of autonomy in the classroom, mostly in the sense of non-interactive education.
- Poor sense of competence given in the classroom, in terms of an absolutely non-personalized teaching methodology.
- Poor sense of relevance in terms of a disconnect between classroom subjects or topics and prior learning experience or values.
On the flip side, engagement takes learning environment to a new level. Engaged students are more curious, focused, and participative when you flip all the factors given above upside-down. We will talk about them in detail in the strategy section.
Engagement builds community
Not feeling connected or cared for, results in highly disengaged students with no sense of community.
Such students may not feel liked in the classroom, have little positive social interaction with peers and teachers, and may also believe the teacher lacks enthusiasm and commitment.
On the other hand, with the right engagement techniques, you can develop a deep sense of community and connect with students. This can help in the overall sense of belonging and student experience encouraging more students to go through with college and complete their higher education.
Graduation rates are directly related to the level of engagement
Research shows a direct correlation between the level of engagement and graduation rates. And not just the graduation rates, better engagement also results in better learning and naturally better test scores.
On the other hand, poor engagement results in students doing the bare minimum, losing interest, bunking classes, and even developing behavioral issues.
So, what are the strategies you can implement to give a boost to student engagement in higher education? Well, let us get to it then!
7 College Student Engagement Strategies That Work
#1. Help students set clear goals
A lack of educational goals gives birth to feelings of stagnation, lack of motivation, and purpose. Goals clearly tell the students what they need to achieve and give them a sense of direction.
So, setting goals is indispensable for higher-ed students, and teachers can help by encouraging them to do so. You can even conduct sessions where students can exchange their goals with each other and help each other achieve them.
A brief guideline on how to set goals can be:
- Set long and short-term goals
- Set reasonable and measurable goals
- Challenge your comfort zone where you can, but take calculated risks
- Make plans on how to achieve them
- Evaluate at intervals and also at the final deadline
Don’t forget to make failure acceptable as part of success itself.
#2. Make education interactive
Higher education students are ideally full of zeal and keen to share ideas and break barriers. Teachers must provide such opportunities to make the education interactive and challenge their learning.
This will inspire self-reflection and also encourage students to learn more and better, bringing student autonomy. Some ways in which you can implement interactive learning are:
- Online discussion forums
- Small group tasks
- Learning activities and assessments
- Design social interactions both inside and outside the classroom environment
Give your feedback and also take their feedback frequently. Later you can implement this feedback to make these interactions richer in multiple ways.
#3. Engage with them in a way they already like
In higher education, interaction must extend beyond the classroom and you must easily connect with your students on every front. For example:
- Career counseling
- Financial Aid
- Health service queries
- Answering questions beyond office hours
- Addressing repetitive queries, etc.
And the best way to do this is to connect with them on chat. Yes, the most natural and popular way that the young generation connects with each other.
The cool thing is that by choosing the right live chat tool, you can start chatting with your prospective students within minutes. Great tools like Social Intents let you integrate live chat with your favorite apps like MS Teams directly.
With this integration, you can start connecting with your students on every subject, without spending any money on training your executives.
#4. Use Social Media platforms and apps to deepen engagement
Higher-ed can no longer afford to have a status website and dysfunctional social media. You must be interacting with your students where they hang out and in the ways they prefer.
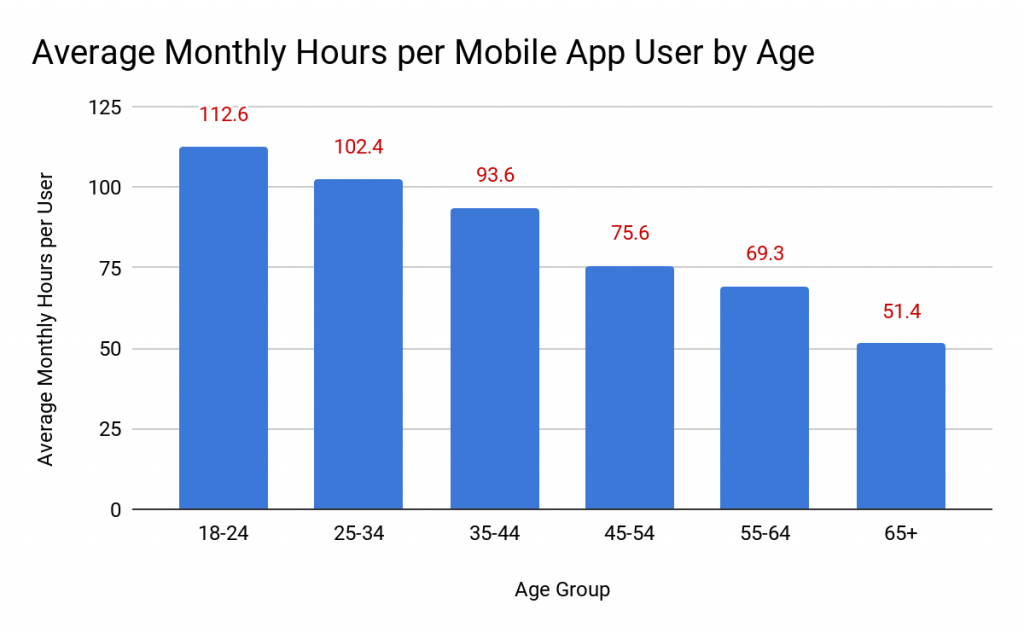
Look at these figures about mobile app usage by age. Surely the age group you are catering to has the highest app usage and so will be happy to interact on one. In fact, the online forums that we discussed to increase engagement can be more successful on an app.
Also, make your website mobile responsive even if you do not have an app.
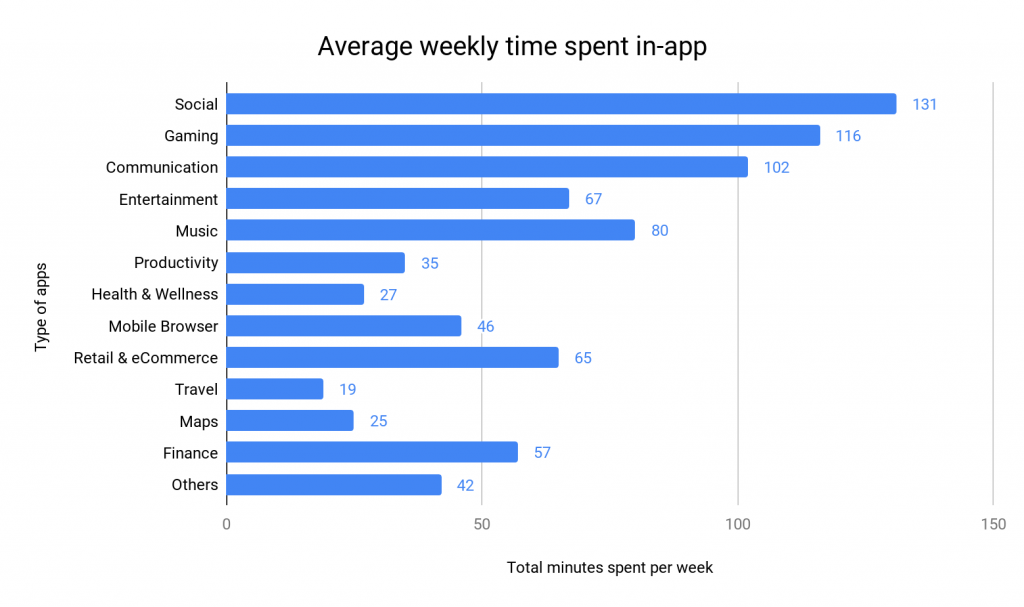
Also, looking at the above image, you can be certain where people are spending most of their time on apps. Social media.
Having a strong social media presence can totally change the game in your favor and strengthen your image as a fun-loving institution. It is also a great way to foster a sense of camaraderie among students and share their college experiences.
Here is an example:
#5. Use the right motivation
Earlier in this article, I discussed using intrinsic and extrinsic motivation tactics to improve student engagement. So, let me elaborate on them now.
Extrinsic or external motivation is when an external reward, for example, accolade, merit, entry into scholarship or accelerated programs, etc. drives the student.
Intrinsic or internal motivation comes into play when it is about something that is interesting or rewarding to the students from the inside. It is when the student is motivated by internal wishes or desires to learn and grow.
Teachers should use both these strategies from time to time for a good mix of engagement.
External motivation works in the short term and may come in handy to give sudden boosts in engagement. While intrinsic motivation keeps students engaged for the long term and you must implement it wisely by encouraging competence, connection, autonomy, etc.
#6. Make learning easy and fun
Education tactics should address the most important challenges of any given time, thereby making learning easy for everybody. The biggest challenge of our times is attention spans.
The popular opinion is that the attention span of college students is somewhere between 10-15 minutes. Case in point, the famous TED talk lecturers are given a maximum of 18 minutes to present their topic, so the impact remains.
It is therefore a good idea for colleges and universities also to break content into chunks. Even if you need to go deep into one topic, you must introduce new content at intervals, allowing breaks in between to keep the engagement going.
Do not forget to use engaging formats like video and multimedia presentations for online learning courses and even for on-campus classes to make things more interesting.
#7. Embrace an inclusive teaching model
To foster a sense of belonging in non-traditional students and also black and Hispanic students, you must develop an atmosphere of inclusion strategically. Typically, 4 types of engagements can encourage them in the right way:
- Financial aid specialists need to step out of their traditional role to help them find the best solutions.
- Transition advisors to help non-traditional students successfully acclimate to the campus.
- Supportive student organizations must find ways to provide support by sponsoring book exchange programs, creating babysitting networks, and hosting informative sessions, making it easier for them to navigate the college experience.
- Counselors can help them deal with a variety of issues, including divorce, bankruptcy, death of a loved one, addiction, stress-related illness, etc.
Conclusion
I hope that by implementing the most relevant strategies given above, you will be able to boost engagement in your institution.
Good luck!
