Banks are transforming how they serve customers, and artificial intelligence is driving that change. Right now, AI tools are answering routine questions in seconds, proactively alerting customers about account issues, and delivering personalized support that wasn't possible just a few years ago.
Industry analysts predict that up to 95% of customer interactions may be AI-powered by 2025, showing just how fast this technology is becoming essential to customer service.
For banks, the stakes couldn't be higher. Done right, AI can vastly improve customer experience while delivering massive cost savings. Research suggests AI could reduce costs by $300 billion globally for banking and finance when fully leveraged. But getting there requires understanding what works, what doesn't, and how to implement AI in a way that actually helps your customers and your team.
This comprehensive guide explores the current state of AI in banking customer service, real-world examples from leading banks, key benefits and challenges, and how to successfully implement AI solutions in your financial institution. Whether you're just starting to explore AI or looking to enhance your existing capabilities, you'll find actionable insights and practical guidance here.
Why Are Banks Using AI for Customer Service?
Banking has always been a 24/7 business. Customers need to check balances or report lost cards at any hour. AI-powered customer service tools are enabling "always-on" support that simply isn't feasible with human staff alone.
Here's why banks are investing heavily in AI for customer service:
24/7 Customer Support Without Hiring More Agents
AI chatbots never sleep. They can instantly answer queries at any time, reducing wait times and providing help even outside normal branch hours. This on-demand support meets modern customer expectations for convenience.
Key Finding: Surveys show that 64% of customers rate 24/7 availability as the best feature of chatbots, and a majority would rather get an immediate chatbot response than wait for a human agent.
Social Intents enables this kind of always-available support by integrating AI chatbots directly with your existing collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, and Webex. Your team can respond to customer chats from the tools they already use, while AI handles the routine inquiries that don't require human intervention.
How to Resolve Customer Issues 87% Faster with AI
AI speeds up service significantly. Intelligent virtual agents can handle simple requests like password resets or balance inquiries in seconds, far faster than a call center could manage. Even for more complex issues, AI assists human agents by fetching information or suggesting solutions in real time.
Studies have found that deploying AI in support can reduce average resolution times by as much as 87%, and enable agents to resolve issues 44% faster by automating routine steps. When Bank of America introduced its AI assistant "Erica," it observed significantly faster support. Erica now handles over 58 million interactions per month, taking pressure off phone lines and helping customers get answers instantly.
How AI Reduces Banking Customer Service Costs by 12X
For banks, customer service represents a major cost center, but AI is changing that equation. Automated interactions are far cheaper per instance than live service. On average, a chatbot interaction costs around $0.50, versus $6.00 for a human agent. That's a 12× difference in cost.
At scale, those savings are enormous. Analysts project that conversational AI will save contact centers about $80 billion in labor costs by 2026. In practice, this means banks can handle a much higher volume of customer queries without a linear rise in headcount or expenses.
AI agents can concurrently chat with thousands of customers at once. This scalability is crucial during peaks like fraud scares or service outages when call centers traditionally get overwhelmed. With AI absorbing the repetitive inquiries, human bankers are freed to focus on higher-value conversations that require empathy and complex problem-solving.
Why AI Delivers More Consistent Service Than Human Agents
Unlike humans, AI doesn't have bad days. It gives the same level of service at 2 AM as at 2 PM. A well-trained AI assistant will provide accurate information based on the bank's data and policies every time. This consistency builds trust with customers.
It also reduces errors. For example, if a policy update is made, the AI can uniformly apply it to every customer query, whereas human agents might provide inconsistent answers until fully briefed. As long as the underlying data is correct and up to date, customers get reliable information on fees, rates, transactions, and more.
Consistency is especially valuable in banking, where mistakes can have serious consequences.
How Banks Use AI to Personalize Customer Service at Scale
Modern AI isn't just a FAQ bot. It can analyze customer data to personalize interactions. Banks are using AI to tailor recommendations and insights to each customer's behavior. For instance, a smart chatbot might alert a customer: "Your credit card bill is due in 3 days. Would you like to pay it now?" or notice spending patterns and suggest budgeting tips.
This level of personalization makes customers feel understood and valued. According to industry research, 70% of banking customers believe AI can make support more personalized and effective.
AI can also proactively reach out with useful alerts. For example, it might notify a user of unusual account activity or a low account balance before it becomes a problem. This turns customer service into a two-way relationship where the bank is actively helping customers stay on top of their finances. Bank of America reported that Erica has delivered over 1.7 billion proactive insights like spending alerts and savings opportunities to customers, helping them manage money better.
What Customer Satisfaction Scores Tell Us About AI in Banking
Speed, convenience, and personalization all add up to happier customers. Many routine banking questions or transactions are things people don't want to spend much time on. They'd prefer to get it done and move on. AI enables that kind of effortless experience.
Impact Data: When done well, 80% of customers report positive experiences with AI chatbots in customer service, and companies have seen customer satisfaction scores increase by 10-12% on average after adding AI assistance.
Also important: AI boosts human agents' effectiveness. By automating the tedious parts of support, agents can focus on empathy and complex problem-solving, which improves overall service quality. The ideal approach is using AI to augment human support, not replace it.
How AI Makes Bank Employees More Productive
While customer-facing benefits get most of the attention, AI also helps bank employees behind the scenes. Intelligent agent-assist tools can listen to customer calls or chats and surface relevant information or suggested responses in real time, saving agents from digging through databases. AI can auto-complete after-call summaries or handle simple follow-up tasks.
This reduces agent workload and burnout. In fact, 83% of support employees say AI's decision-making support is a major advantage, and agents report saving over 1 hour per day by using AI tools for routine tasks. By taking away the grunt work, AI lets human bankers focus on more meaningful interactions, which makes their jobs more engaging.
Of course, these benefits only materialize if the AI is done thoughtfully. Poorly executed chatbots can frustrate customers (and we've all experienced clunky bots that don't understand us). The difference between success and failure often comes down to choosing the right platform and following proven best practices.
What Can AI Chatbots Do in Banking Customer Service?
AI is a broad field, but in banking customer service, the most visible form is the chatbot or virtual assistant. These are AI-powered conversational agents that communicate with customers via text (on websites, mobile apps, or messaging platforms) and sometimes via voice. Banks worldwide have launched chatbots to handle a range of customer service tasks.
Here are the most popular applications of AI in banking customer service:
How AI Answers Banking FAQs Instantly
This is the entry-level use case for AI in support. Chatbots can instantly answer frequently asked questions about branch hours, ATM locations, routing numbers, or how to reset a password. They can also provide up-to-date account information on request, such as balances or recent transactions.
By handling these simple queries, AI reduces the load on call centers and lets customers get info without waiting. For example, customers can ask, "What's my checking account balance?" or "How do I update my mailing address?" and get an immediate answer from the bot. If the question is too complex, the bot can escalate to a human.
Many banks report that 70-80% of routine questions can be resolved by automated chat agents, reserving human reps for more complex issues.
How Customers Perform Banking Transactions Through AI Chat
More advanced banking bots go beyond Q&A to actually perform transactions for the customer. This includes things like:
→ Transferring funds between accounts
→ Checking loan payoff amounts
→ Making a payment
→ Temporarily blocking a lost credit card or resetting a PIN
For instance, a customer might type, "Please transfer $500 from my checking to savings," and the AI assistant will carry out the request securely after verifying user identity. Bank of America's Erica can handle a variety of account tasks end-to-end in the chat interface, including Zelle transfers, bill payments, card management, and more, without forcing the user to navigate menus or call support.
By integrating with core banking systems, the AI essentially becomes another front-end for banking transactions. This is highly convenient for customers and cuts down on calls or branch visits. Seamless integration is key because the chatbot needs secure access to account data and transaction systems to fulfill these requests in real time.
How AI Chatbots Prevent Missed Bill Payments
Missing a payment can be costly for customers and banks alike. AI assistants help avoid that by reminding customers of upcoming bills and even facilitating bill payments directly through chat.
For example, a chatbot might say, "Your electric bill of $150 is due tomorrow. Would you like to pay it now?" If the customer replies yes, the bot can process the payment instantly through the linked account or card.
Similarly, bots can nudge customers about credit card due dates, loan EMIs, or any recurring payments. Customers appreciate these gentle reminders and the ability to handle the payment on the spot, which saves them time and prevents late fees. On the bank's side, this leads to fewer delinquencies.
Banks can also allow customers to schedule payments or set up autopay via the chatbot. By making bill pay as easy as sending a text, AI enhances the customer's financial management.
How AI Detects Banking Fraud in Real Time
Security is paramount in banking, and AI is playing a big role in safeguarding customers. A prime example is real-time fraud alerts delivered by chatbots. Capital One's AI assistant "Eno" will automatically message customers if it detects a suspicious transaction attempt. For instance, it might ask: "Did you just try to spend $200 at XYZ Electronics? Reply YES or NO." If the customer replies no, Eno can guide them through securing the account.
Eno can even proactively generate virtual credit card numbers for online shopping, adding a layer of fraud protection by not exposing the real card number. These AI-driven security features increase customer trust by showing that the bank is watching out for them.
Also, chatbots can help with password resets or unlocking accounts after suspected fraud flags, using secure authentication steps. The immediacy of AI alerts (often via push notification or SMS) means potential fraud is noticed within seconds, not hours, which can dramatically reduce unauthorized account usage. Customers have peace of mind knowing an intelligent assistant is monitoring their accounts 24/7.
How AI Streamlines Loan and Credit Card Applications
Applying for a loan or credit product often requires providing information and waiting for approval, a process that can be improved with AI. Some banks use chatbots to pre-screen and guide customers through loan or credit card applications.
The chatbot can ask questions to determine eligibility (income, desired loan amount, etc.), answer the applicant's questions about rates or terms, and even fill out the application forms interactively. For example, the bot might ask, "Are you interested in a personal loan or auto loan?" followed by, "What loan amount are you looking for?" It's essentially doing the initial interview that a bank officer might do, but on the customer's schedule.
The AI can then either give an instant preliminary decision (if the bank's systems allow that) or forward the info to human underwriters and later provide status updates. This streamlined approach increases application completion rates and ensures a positive customer experience. Some banks have reported higher completion rates when using chatbots because the interactive Q&A format keeps users from abandoning lengthy web forms.
How AI Speeds Up Banking KYC and Account Opening
Bringing a new customer onboard involves a lot of information collection and verification. AI can streamline this significantly. Know Your Customer (KYC) and account onboarding bots walk new customers through the required steps and paperwork in a chat conversation.
Instead of making a customer fill out multiple paper forms or static online forms, a chatbot can request needed documents (photo ID, proof of address) by simply having the user snap a picture or upload a file in the chat window. The AI can automatically read and validate the documents using OCR and verification algorithms, immediately flagging if something is missing or unclear.
For instance, the bot may prompt: "Please upload a photo of your ID for verification." Once uploaded, it checks that the image is legible and meets the requirements, then confirms to the user that the ID is accepted. This real-time feedback prevents delays (no waiting days only to find out a document was wrong).
The chatbot can also gather personal details, have the user e-sign agreements, and answer any questions about the process. By digitizing KYC via AI, banks reduce manual data entry and compliance processing on their end, and new customers enjoy a smoother sign-up experience. Compliance is assured because the bot doesn't forget required steps, and it maintains a transcript and records of all customer-provided info in a secure manner.
How AI Chatbots Teach Customers About Financial Management
Some banks use AI to help customers become more financially savvy. AI chatbots can serve as personal financial coaches, providing tips on budgeting, saving, or credit management in a conversational way.
For example, a customer might ask, "How can I improve my credit score?" and the bot can reply with personalized pointers (like paying down certain balances) or resources. Or if a user says, "I want to start saving for a house," the bot could break down a savings plan or suggest an appropriate savings account.
A few banks have even gamified this advice. The chatbot sets savings goals and tracks progress, sharing encouraging updates. All of this helps customers feel their bank is a partner in their financial journey, not just a transaction facilitator.
But trust in AI for complex financial advice remains a work in progress. Only about 27% of customers say they trust AI for financial advice over a human advisor. So, most AI "advice" today is confined to basic personal finance guidance or product recommendations, rather than high-stakes investment advice. Still, by offering on-demand education, banks can increase customer engagement and loyalty.
How Banks Serve More Customers with Multi-Language AI
AI is also helping banks serve a more diverse customer base. Chatbots can be designed to converse in multiple languages, switching easily based on the user's preference. This is incredibly useful in markets or regions with bilingual populations, or for large banks that serve customers across different countries.
Instead of maintaining separate call centers for different languages, a single AI system can handle inquiries in Spanish, English, Mandarin, Hindi, or any language it's trained on. For example, Singapore-based DBS Bank's "Digibot" serves customers in both English and Chinese, reflecting its user base. This multilingual capability has strengthened DBS's appeal in Asia's diverse markets.
AI can also improve accessibility for customers with disabilities:
• Voice-activated assistants help visually impaired customers check balances or make transactions using speech
• Bots can be made compatible with screen readers
• Simple language for those with cognitive impairments
• Voice and chat interfaces for those who can't use a phone keypad easily
By making digital banking more accessible, AI enables financial inclusion, allowing all customers to get service without barriers. Banks that prioritize this aren't only doing the right thing but also expanding their potential customer pool.
How Banks Use AI to Support Their Own Employees
While not customer-facing, it's worth noting that many banks use AI chatbots internally to assist their own employees (for IT support, HR queries, etc.). For example, Bank of America has an "Erica for Employees" that helps its staff with tech support and common inquiries, reportedly handling 90% of employee questions and cutting internal help-desk calls by half.
This indirectly benefits customers because bank employees can get their issues resolved faster and stay focused on serving clients. Plus, AI can triage customer service requests (classifying emails or chat intents) and route them to the right department or suggest next steps to agents. All these applications improve the overall efficiency of the bank's service operations.
In summary, AI in banking customer service ranges from the simple (answering FAQs) to the sophisticated (completing complex tasks like loan applications or fraud prevention). Not every bank's chatbot does all of the above. Capabilities vary. In fact, as of late 2024, only about 2.7% of banks had advanced chatbots that handle complex queries with AI, while roughly 38% had very basic bots and the rest had none at all. This means there's plenty of room for growth.
Best Banking AI Chatbot Examples That Actually Work
Many leading banks have developed their own AI-powered customer service assistants, often giving them friendly names. Here are three of the most notable examples and what makes them successful:
Bank of America's Erica: What 3 Billion Interactions Taught Us
When it comes to banking chatbots, Bank of America's Erica is often cited as one of the most advanced and widely used. Launched in 2018, Erica has quickly grown to serve nearly 50 million users.
By August 2025, Erica surpassed 3 billion total client interactions, averaging about 58 million interactions each month. To put that in perspective, Erica is engaging with customers on a scale that far exceeds what BofA's human workforce could handle alone.
What Erica Can Do:
① Checking balances
② Transferring money
③ Scheduling bill payments
④ Ordering a new card
⑤ Providing credit score updates
⑥ Analyzing spending patterns
All of this happens through a chat interface in BofA's mobile app or website. Customers might ask, "How much did I spend on groceries last month?" and Erica will instantly analyze transactions and give the answer. Or a user could type, "I lost my card," and Erica will guide them through locking the card and ordering a replacement, all in one conversation.
Proactive Innovation: One of Erica's strengths is proactive customer service. It doesn't just wait for questions. It also provides personalized insights and alerts. Bank of America reported that clients have received over 1.7 billion proactive insights from Erica, helping them spot things like unusual spending, upcoming bills, or opportunities to save money.
Most importantly, Erica has delivered concrete results in customer service efficiency. According to Bank of America, over 98% of users get the answers or help they need from Erica, significantly reducing calls to the contact center. When so many inquiries are resolved by the AI, human agents have more time to dedicate to complex issues that truly need a human touch.
The key to Erica's success has been strong natural language processing (so it understands a variety of phrasings), deep integration with BofA's systems (so it can actually do things like transactions), and a design philosophy of adding value. By investing early and continually in AI, Bank of America positioned itself as a leader in digital banking service.
Capital One's Eno: How AI Prevents Banking Fraud
Capital One's virtual assistant is named Eno (which, fun fact, is "One" spelled backwards). Eno is designed with an emphasis on security, account monitoring, and customer peace of mind.
Security-First Features:
Eno is always watching out for the customer's financial well-being. It sends real-time alerts for anything unusual on the account. For example, if there's a suspicious transaction or a duplicate charge, Eno might ping the customer: "I noticed a charge that looks odd. Was this you?" and guide them if it wasn't. Capital One has highlighted how Eno helps catch fraud or mistakes early, potentially saving customers money and hassle.
Eno also monitors for things like when a free trial is about to convert to a paid subscription, notifying the user so they aren't caught by surprise. This is an extremely handy service in today's subscription economy.
Another standout feature is virtual card numbers. Eno can instantly generate unique, disposable credit card numbers for Capital One cardholders to use when shopping online. This is built right into the browser via an extension. Eno will pop up when you're on a checkout page and offer to create a virtual card number. Using a virtual number means if that merchant's data is ever breached, your real card info isn't exposed.
Eno can do the usual things too, like answer questions about your balance, help you pay your Capital One bill, or track your spending. It often communicates with a bit of personality (Eno is known for sending fun texts like using emojis to confirm payments). Capital One's tone is meant to be friendly and reassuring, to build trust with users who might be wary of a "robot banker."
Capital One hasn't publicly shared as many numbers as BofA, but they've stated that Eno has helped increase customer trust by proactively protecting accounts and providing useful insights. Features like the fraud alerts and virtual cards give customers a sense that the bank is being proactive and innovative in protecting them.
DBS Bank's Digibot: Multi-Language Banking AI Success Story
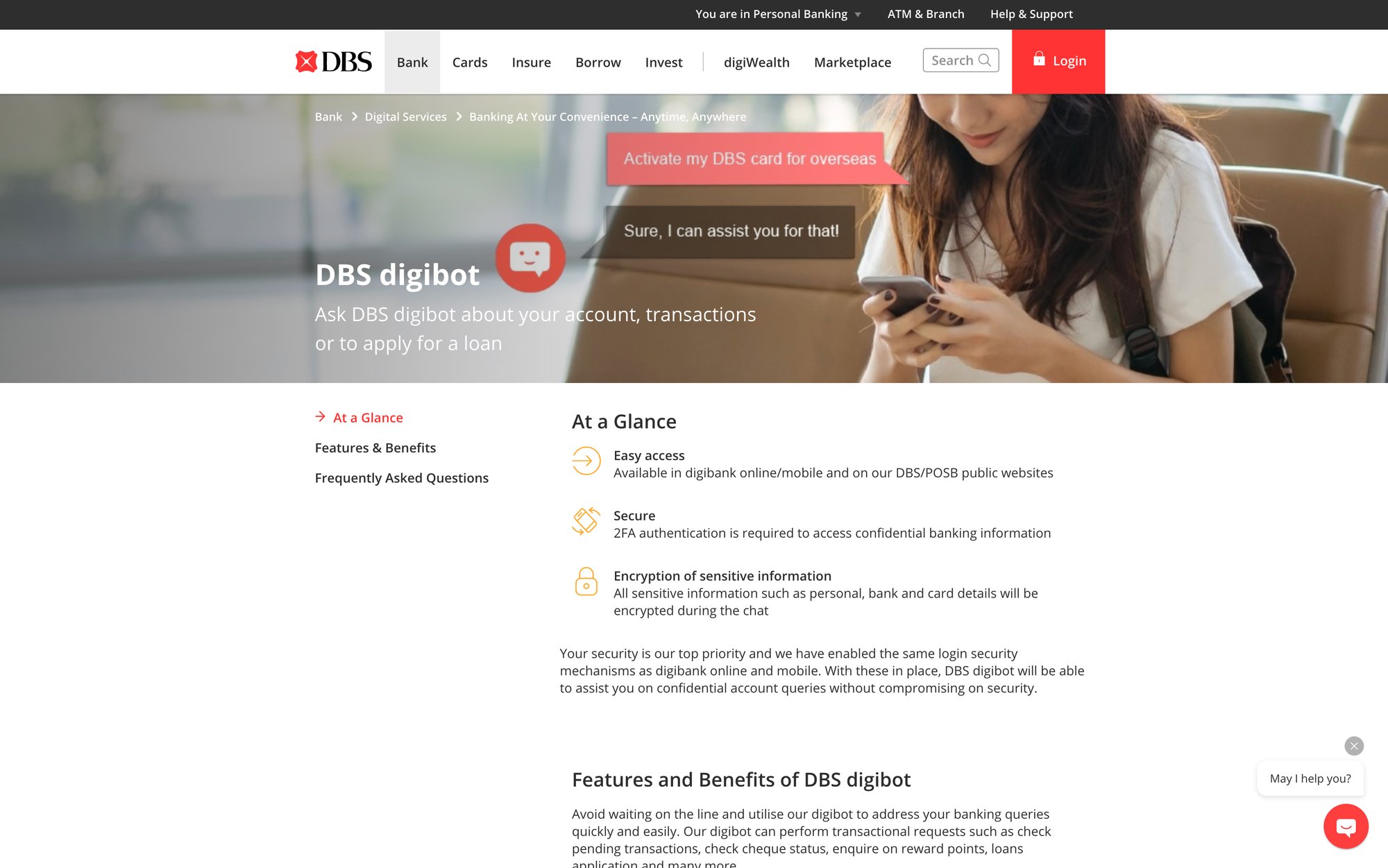
Not only U.S. banks are using AI. In Asia, a great case study is DBS Bank's Digibot. DBS is a large bank based in Singapore, and Digibot is their virtual banking assistant that serves customers across their digital platforms.
Multilingual Excellence:
Digibot is available 24/7 on the DBS website and mobile app, handling a wide array of customer requests. Customers can ask Digibot things like, "How do I reset my ATM PIN?", "Show me my last 5 transactions," or even start processes like "I want to apply for a personal loan." The bot can walk the user through these steps or direct them to the right self-service module.
By taking care of such routine service needs, Digibot frees up human customer service agents to focus on more complex issues. DBS has noted that this automation has improved their operational efficiency and allowed their staff to concentrate on higher-level customer care.
One of Digibot's distinguishing features is multilingual support. Singapore's population is multilingual (English, Chinese, Malay, Tamil are common languages there), and DBS serves other countries as well. Digibot converses in both English and Mandarin Chinese, catering to a broad customer base. This capability required training the AI in different languages and understanding region-specific queries, but it paid off by making the service accessible to more customers in their preferred language.
Another aspect is channel integration. Digibot isn't just a pop-up on the website. It's built into DBS's online banking and mobile app interfaces for a seamless omnichannel experience. Whether a customer is on their phone or laptop, Digibot is ready to assist, and it maintains context across channels.
| AI Assistant | Bank | Launch Year | Key Strength | Notable Metric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erica | Bank of America | 2018 | Scale & proactive insights | 58M monthly interactions, 3B total |
| Eno | Capital One | Earlier | Security & fraud prevention | Virtual card numbers, subscription alerts |
| Digibot | DBS Bank | N/A | Multilingual support | English & Mandarin, 24/7 availability |
While specific performance stats for Digibot aren't widely publicized, DBS has won awards for digital innovation, and the chatbot is credited with contributing to DBS's high customer satisfaction ratings in digital banking. Digibot's success underlines the importance of localizing AI services. By offering bilingual support and embedding in the local digital ecosystem, DBS made AI a natural extension of their customer service.
These examples show that AI in banking customer service isn't theoretical. It's happening now, at scale, in some of the world's largest financial institutions. Bank of America's Erica shows how AI can handle volume and provide personalized finance guidance at once. Capital One's Eno shows the power of focusing AI on security and customer financial health. DBS's Digibot shows that a well-done chatbot can elevate service quality and accessibility in a multilingual market.
But not every bank's AI rollout has been smooth. Success depends on more than just turning on a bot.
Common AI Banking Customer Service Challenges (And How to Solve Them)
For all the enthusiasm about AI, it's important to acknowledge that deploying it in banking customer service comes with challenges. A poorly done AI can annoy customers, erode trust, or even pose security risks. Here are the key challenges banks face with AI in customer service and best practices to overcome them:
How to Fix AI Chatbots That Don't Understand Customers
Early chatbots were notorious for misunderstanding users because human language is complex. Banking customers might ask the same question a dozen different ways ("What's my balance?" vs. "How much money do I have?" etc.). If the AI can't parse it, the experience falls flat.
Best Practice: Banks must use advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) engines and continuously train them on real customer phrasing. Start with a robust NLP model (potentially using modern large language models or generative AI fine-tuned on support data) so the chatbot can handle synonyms, slang, and context.
It should also handle follow-up questions in context. For example, if a customer asks about "my balance," the bot gives it, then customer says "what about savings?" The bot should infer they're asking the savings account balance now.
Investing in NLP quality directly translates to better customer satisfaction because the bot "gets" what they mean more often. Ongoing training is key. Banks like BofA regularly update Erica based on new kinds of questions being asked. By closing the understanding gaps, the AI becomes more conversational and human-like in its interactions.
How to Connect AI Chatbots to Your Banking Systems
An AI assistant is only as useful as the actions it can perform. If a bot can't access up-to-date account info or execute transactions, it'll be limited to generic FAQs. Banks should ensure their chatbot is tightly built into backend banking systems: core banking database for balances and transactions, CRM for customer profile info, payment systems, loan processing systems, etc.
This often means using secure APIs that the chatbot can call when a user asks, "What's the status of my loan application?" or "Pay my credit card bill." Integration is also crucial for identity verification. The chatbot needs to link to single sign-on or authentication services so it knows who it's talking to (after the user logs into the app or answers security questions).
Many early bank bots failed because they could only provide information that was already on the public website (like branch hours), which isn't very compelling. The best AI deployments, like Erica or Digibot, have read and write access (with proper security controls) to the bank's internal systems, enabling them to give real-time, account-specific answers and perform transactions on behalf of the customer.
Achieving this integration might require significant IT work and coordination across departments, but it's absolutely necessary for a "virtual assistant" rather than just a "Q&A bot."
How Banks Ensure AI Customer Service Meets Compliance Requirements
Banks operate in a highly regulated environment, and any customer-facing AI must rigorously protect data privacy and comply with financial regulations. This is non-negotiable. Best practices include end-to-end encryption of all chatbot communications (so nobody can snoop on a conversation that might include account numbers or personal data).
Data handled by the AI (whether it's stored chat transcripts or any analytics) should be stored securely and in compliance with regulations like GDPR (in Europe) or CCPA (in California). If the AI connects to payment systems, it may need to comply with PCI DSS standards for handling payment card information.
Banks should also ensure the AI follows proper authentication flows. For example, a chatbot should not reveal sensitive account details until it has verified the user's identity through login or security questions, just as a human rep would.
Compliance extends to things like auditability. Banks might need logs of what the AI told customers, especially if any advice or decision is made automatically. Regulators have interest in AI decisions (for instance, if an AI denies a loan application, that needs to be explainable under fair lending laws).
In sum, incorporating your compliance and cybersecurity teams early in the AI project is a must. It's also wise to be transparent with customers that they're interacting with an AI and how their data is used. Doing all this builds trust.
As one banking report noted, lack of trust is still a barrier. Only 27% of customers said they currently trust AI for financial advice, and concerns around data security are one reason. By designing AI with privacy, security, and transparency from the start, banks can mitigate these issues.
How to Build Customer Trust in Banking AI
Beyond technical factors, there's a human factor: customers need to feel comfortable using the AI. Some customers (especially older generations) are hesitant to chat with a bot, or may have had bad experiences with early bots that couldn't help them. According to a recent survey, 37% of banking customers said they've never even tried a chatbot, often due to lack of awareness or interest.
And many who did try early bots found them underwhelming for anything beyond basic queries. To overcome this, banks should educate customers about the AI's capabilities and limitations, and make it easy to access a human when needed.
It's crucial not to trap users in an endless chatbot loop. That's a top complaint. In fact, 74% of banking customers said they still prefer a human agent for simple queries because they worry the bot might not handle it or they just feel more comfortable with a person. That statistic shows that even for routine stuff, people value the option of a human.
Best practice: design the chatbot with a seamless escalation to human agents at any point the user is frustrated or the AI isn't confident about the answer. For example, if the AI senses confusion ("I'm not sure I got that. Let me get a human for you.") or if the customer types "agent" or "representative," it should immediately pause, transfer the conversation (with context) to a live person, and inform the user someone will help shortly.
Importantly, when handing off, pass the conversation transcript and data to the human so the customer doesn't have to repeat themselves. Many banks build their chatbot with live chat software or CRM systems so that this handoff is smooth.
By doing this, customers learn that using the chatbot is low-risk. If it can help, great. If not, a person is right there. Over time, as the AI proves itself by handling many questions well, trust will build and more customers will actively choose the bot first.
How to Personalize Banking AI Without Invading Privacy
Customers expect banks to know them and tailor service accordingly. AI makes that possible at scale (as we discussed with personalized insights). But there's a fine line: some customers might feel creeped out if the bot appears too knowledgeable or intrusive.
For instance, a chatbot proactively saying "I see you're near an auto dealership, need a car loan?" might cross the line. Banks should use AI-driven personalization thoughtfully and opt-in where appropriate.
Providing personalized budget tips based on spending is likely welcome, especially if the customer signed up for "financial insights." But using AI to cross-sell products must be done in a helpful, not pushy, manner. One approach is to focus personalization on genuinely service-oriented messages (like fee avoidance alerts, savings opportunities) more than purely marketing offers.
If marketing offers are served, AI can ensure they're relevant. Also, always allow customers to turn off certain notifications if they want. Overall, personalization should feel like the bank is looking out for the customer's interests, not just the bank's sales targets. When done right, it increases satisfaction. AI-tailored recommendations have been linked to a 27% boost in customer satisfaction in some studies.
How to Modernize Legacy Banking Systems for AI
Many banks, especially older ones, still operate on legacy IT systems that aren't readily compatible with modern AI tools. Data might be siloed across mainframes and disparate databases, making integration a challenge. In fact, research found that 61% of companies across industries aren't fully ready data-wise for AI. Their data isn't accessible or clean enough.
Banks should invest in data modernization as part of their AI projects: consolidating customer data, cleaning it, and setting up APIs to access it. This often involves internal IT transformation beyond just the chatbot itself. It's a challenge, but those who overcome it gain an edge.
An AI assistant is only as "smart" as the data feeding it. If a bank's customer records are incomplete or updated only batch overnight, the AI might give wrong answers (like not reflecting a payment made an hour ago). Real-time data infrastructure is ideal. Some banks tackle this by using middleware that pulls together various systems for the AI to interface with. The bottom line: don't underestimate the backend work needed to make an AI front-end shine.
How to Measure and Improve AI Banking Performance
Launching an AI service isn't a "set and forget" endeavor. Banks need to continuously measure how the AI is performing: what percentage of inquiries it resolves, how customers rate those interactions, how often it had to escalate, etc.
Useful metrics include:
• Containment rate (chats not needing human escalation)
• CSAT for bot interactions
• Average handle time
• Impact on call volume
Collecting user feedback (many bots ask "Did that answer your question?") can pinpoint where it's failing.
With these insights, banks can iteratively improve the bot's knowledge base and dialog flows. Many banks have dedicated "AI trainers" or teams in their contact centers now, who review transcripts where the bot faltered and then adjust the bot's responses or add new content to address those gaps.
This continuous improvement cycle is a best practice that keeps the AI relevant and helpful as products, policies, and customer expectations change. It's also wise to periodically update the AI's underlying model. For example, some banks are now upgrading their bots with generative AI capabilities to make them even more conversational and to handle unexpected queries better.
But doing so carefully (with human oversight and testing) is important to avoid AI that "hallucinates" answers. The field is moving fast, so successful banks treat their AI as a living project, not a one-time IT deployment.
How to Market AI Features to Your Banking Customers
Finally, a softer aspect: let your customers know what your AI assistant can do for them. Sometimes adoption is low simply because customers aren't aware of new features or assume the bot is only for very basic tasks.
Banks have found success in marketing their AI as a value-added service. For example, highlighting in emails or ads, "Meet [Bot Name]: your 24/7 personal banker." Teach customers through simple examples that they can ask it to do XYZ. Include demos or tooltips in your app when the chatbot first launches, like showing sample questions.
The more customers know about the AI's capabilities (and limitations), the more effectively they'll use it. This manages expectations and drives usage to the areas the AI handles best, leading to more positive outcomes. In short, build it and promote it.
When banks follow these best practices (robust NLP, deep integration, strong security, easy human handoff, personalization with care, data readiness, continuous improvement, and good communication), they set themselves up for AI success. It turns the chatbot from a gimmick into a genuine enhancement of the customer experience.
Remember, the goal isn't to replace humans but to elevate the service overall. The best customer experiences come from blending AI and human expertise together.
Social Intents: How to Deploy Banking AI Customer Service in Days, Not Months
Understanding the challenges of doing AI in banking customer service, Social Intents was built specifically to solve these pain points. While large banks like BofA can spend millions building custom AI assistants, most financial institutions need a solution that's fast to deploy, easy to manage, secure, and cost-effective.
Social Intents delivers exactly that. Here's how:
Deploy AI Banking Chatbots Without Writing Code
One of the biggest barriers to AI adoption is the complexity of doing it. Many banks hesitate because they assume it requires a massive IT project, custom development, and months of integration work.
Social Intents changes that equation entirely. The platform is designed for no-code setup, meaning you can launch a fully functional AI chatbot without writing a single line of code. Your business users can configure the bot, train it on your content, and deploy it across your digital channels in a matter of days.
This speed matters. While your competitors are still planning their AI strategy, you can be delivering AI-powered customer service. You can start small (perhaps with FAQ handling), prove ROI quickly, and then expand capabilities as you see results.
How Bank Agents Answer Chats from Teams, Slack, or Google Chat
Remember earlier when we discussed how AI helps employee productivity? That only works if your team actually uses the AI tools. Many chatbot platforms require agents to learn yet another interface, which creates adoption friction.
Social Intents solves this by bringing customer chats directly into the collaboration tools your team already uses every day: Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, and Webex.
When a customer starts a chat on your website or mobile app, it appears as a message in your team's channel. Your agents can respond from right there, without switching contexts or logging into another platform.
This native integration means:
→ Instant agent adoption (no new tool to learn)
→ Faster response times (agents see chats where they already are)
→ Better collaboration (team members can easily help each other with complex inquiries)
→ Lower training costs (agents already know how to use Teams or Slack)
For banks with agents who spend their days in Teams or Slack anyway, this is transformative. It's the difference between AI that works with your workflow versus AI that fights against it.
How to Transfer Customers from AI to Human Agents Seamlessly
One of the most critical best practices we discussed was smooth escalation from AI to human agents. This is where many chatbot setups fail. Customers get frustrated when they're trapped in an AI loop that can't help them, or when they finally reach a human who has no context about what they've already discussed.
Social Intents excels at this handoff. The platform supports seamless human escalation where the AI automatically transfers the conversation to a live agent when needed, along with the full conversation history.
Your agents receive the chat with complete context: what the customer asked, what the AI suggested, where the AI got stuck. The customer doesn't have to repeat themselves. This creates a smooth, professional experience that builds trust.
You can configure when handoffs occur:
① AI-first approach: AI handles as much as possible, escalates only when necessary
② Hybrid approach: AI and humans work together on every conversation
③ AI after-hours: AI handles chats when humans aren't available, then hands off during business hours
④ Confidence-based: AI escalates when it's not confident about the answer
This flexibility lets you optimize for your specific needs and gradually increase AI automation as your confidence in the system grows.
How to Reach Banking Customers Across Every Channel
Today's banking customers expect to reach you through multiple channels. They might start a conversation on your website, continue it via your mobile app, or even prefer messaging through WhatsApp or Facebook Messenger.
Social Intents works across all these channels with multichannel communication support. Whether your customer is on your website, mobile app, WhatsApp, or Messenger, they can get real-time support from the same AI assistant, with conversations maintaining context across channels.
This omnichannel capability is especially valuable for banks because:
-
Younger customers prefer messaging apps (reaching them where they are)
-
Mobile-first customers expect in-app support
-
Website visitors want instant help without phone calls
-
International customers might prefer WhatsApp (common in many countries)
With Social Intents, you deploy once and reach customers everywhere.

How to Connect Banking AI to Your Transaction Systems
Generic chatbots can answer questions, but banking customers often need to take action: check account status, create support tickets, look up transaction details, or process payments.
This is where Social Intents' Custom AI Actions capability becomes powerful. These are custom integrations with your third-party tools and banking systems that enrich chat conversations with real-time data and actions.
For example:
• Account Status: "What's my current balance?" triggers an API call to your core banking system
• Transaction History: "Show my last 5 transactions" pulls real data from your database
• Bill Pay: "Pay my electricity bill" starts a secure payment through your payment processor
• Loan Application Status: "Where's my loan application?" checks your loan processing system
• Card Controls: "Lock my credit card" triggers your card management API
These custom actions transform your chatbot from an information source into a transaction engine. Customers can actually get things done through the chat, not just ask about them.
Customer Interest: According to Social Intents, customers are VERY interested in these capabilities because they directly address the "I want to do something, not just learn about it" use case that drives customer satisfaction.
Banking-Grade Security That Meets Compliance Standards
For banks, security and compliance aren't optional. They're table stakes. Any AI solution you deploy must meet stringent requirements for data protection, encryption, audit trails, and regulatory compliance.
Social Intents was built with these requirements in mind:
-
End-to-end encryption for all chat communications
-
Secure API integrations with your banking systems
-
Audit logs of all AI interactions for compliance requirements
-
Role-based access controls for agent permissions
-
Data residency options for regional compliance needs
The platform can work with your existing authentication systems (SSO, SAML) so the chatbot knows who it's talking to before revealing any sensitive information. And all customer data is handled in compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific requirements.
This built-in security means you're not starting from scratch. You're starting with a foundation that was designed for the financial services industry's unique needs.
Scale Your Banking Team Without Per-Agent Fees
Many chatbot platforms charge per agent, which can get expensive as your team grows. This creates a perverse incentive: you either limit who can help customers (reducing service quality) or pay escalating costs (hurting your ROI).
Social Intents takes a different approach. From the Basic plan upward, you get unlimited agents. This means:
-
Scale your team without scaling costs (add agents freely)
-
Enable broader participation (let specialists jump in when needed)
-
Cross-training opportunities (new agents can observe without licensing costs)
-
Seasonal flexibility (add temporary agents during peak periods at no extra charge)
This unlimited agent model is especially valuable for banks with multiple departments (retail banking, commercial, mortgage, etc.) who all need to handle customer chats in their specialty areas.
What Results Banks See with Social Intents
While we can't share specific client names without permission, Social Intents has helped financial institutions of various sizes achieve:
• 60-80% reduction in routine inquiry handling time
• 24/7 customer support without proportional staffing increases
• Higher customer satisfaction scores through faster response times
• Significant cost savings versus hiring additional call center staff
• Improved agent productivity by handling repetitive questions with AI
The platform is actively used by banks, credit unions, fintech companies, and other financial services providers who needed a solution that balances ease of use with enterprise capabilities.
How to Get Started with Social Intents for Banking
Ready to bring AI-powered customer service to your bank? Here's how simple it is to get started with Social Intents:
① Sign up for a 14-day free trial (no credit card required to start)
② Connect your collaboration tool (Teams, Slack, or use the web console)
③ Add the chat widget to your website or app (simple code snippet or use platform plugins)
④ Train your AI chatbot (upload your FAQ content, knowledge base, or website for automatic learning)
⑤ Set your escalation rules (decide when AI should hand off to humans)
⑥ Go live (start serving customers immediately)
Most banks are fully operational within 3-5 days of signing up. Compare that to the 6-12 months it might take to build a custom solution, and the value becomes clear.
Want to see it in action? Visit Social Intents to start your free trial or request a personalized demo for your bank.
What's Next: The Future of AI in Banking Customer Service
As of 2025, we're seeing rapid change in AI capabilities, and banks are poised to benefit even more in the coming years. Here are a few trends and what they mean for banking customer service:
How Generative AI Will Change Banking Conversations
The advent of powerful generative language models means chatbots are becoming far more fluent and versatile. We can expect bank chatbots to transition from scripted Q&A models to more free-form conversational agents that can understand complex multi-part questions and even handle nuanced tasks.
For example, instead of a customer having to follow a rigid menu ("1 for accounts, 2 for cards…"), they could just write a paragraph describing an issue, and the AI will figure out the intent and respond helpfully. Some banks are already piloting GPT-based assistants to handle email inquiries or assist call center agents in real time.
By 2024, about 75% of banking leaders said they were either deploying or planning to deploy generative AI in the near term, so this wave is coming fast. The challenge will be ensuring these models stay accurate and don't produce irrelevant or non-compliant answers. Expect to see a hybrid approach where generative AI is harnessed but with guardrails (like restricting its output to verified knowledge base information).
If done right, the line between talking to a bot and a human will blur even further, potentially boosting adoption among those who dislike today's primitive bots.
Banking AI That Follows You Across Every Device
We've mostly discussed chatbots in mobile apps or websites, but the future is an AI assistant that follows the customer across channels. That could mean the same AI accessible via popular messaging apps (WhatsApp, WeChat, SMS), smart speakers (imagine asking Alexa about your bank balance and Alexa's pulling info from your bank's AI via an integration), or even in augmented reality interfaces down the road.
Banks will aim to have a unified AI that knows you whether you're on the phone, chat, or voice. This requires strong back-end integration (so that context carries over). We're already seeing banks work with messaging platforms. For instance, some banks have chatbots on Facebook Messenger or WhatsApp to answer questions. The next step is those bots being as fully featured as the one in the bank's own app.
The idea is that wherever the customer seeks support, the AI is there and has the context of past interactions. A practical near-term example: if a customer starts with the chatbot on the website but then calls the support line, the AI could transcribe and analyze the call and feed that info to the human agent or even respond via an IVR system. Silos between channels will break down with AI as the connecting thread.
How Voice AI Will Replace Banking Phone Menus
Speaking of phone calls, many banks still have clunky Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems ("press 1 for this…"). AI is set to make voice service more conversational as well. Voicebots that you can talk to naturally on the phone can replace those phone menus.
Instead of pressing numbers, a caller could explain what they need in a sentence, and a voice AI (using speech-to-text and NLP) will route or answer appropriately. Some banks have started rolling out voice assistants on their 1-800 numbers. Combined with text chatbots, this means whether a customer types or talks, they're interacting with the same AI brain.
Given that a portion of customers (especially older ones) still prefer using the telephone, this is important to ensure AI-driven service doesn't leave anyone out. Advances in speech recognition and natural language understanding are making phone AI much better than a few years ago. We can anticipate that by late this decade, calling your bank and speaking to an AI that sounds almost human will be commonplace.
How AI Copilots Will Make Every Bank Agent a Super-Agent
While we often focus on direct customer-facing AI, a big trend is AI helping human agents in live conversations. For instance, when you're chatting with a support rep on a bank's website, there might be an AI in the background listening (or reading) and feeding the rep suggestions: relevant knowledge base articles, reminders of the customer's profile, even real-time suggested replies based on similar cases.
This is already happening in some contact centers. It effectively makes every agent a "super-agent" with AI backup. The outcome is quicker and more consistent service, even from relatively novice employees. We expect this to become standard. Every bank rep will have an AI copilot. It won't be visible to the customer except in how smoothly the agent can help them.
Also, AI can handle after-call work (automatically writing up call summaries, logging tickets, etc.), saving agents time. Banks that do this might see faster training time for new agents and lower handling times, improving both cost and customer satisfaction. It's the next phase of augmenting humans rather than replacing them.
AI as Your Personal Financial Advisor
As comfort grows, AI assistants could take on more of an advisory role. For example, connecting with personal finance management tools to give holistic advice: "You have an upcoming goal to save for a vacation. I suggest moving $100 to savings now," or working with investment accounts to answer questions about portfolio performance.
Some wealth management firms already use AI to assist advisors or even directly interface with clients for basic questions. In retail banking, AI might guide customers towards better decisions (with appropriate disclaimers that it's not a human financial advisor).
The line between customer service and financial advice might blur in low-stakes scenarios (like everyday budgeting or product recommendations). If regulations allow and trust builds, AI could become a primary touchpoint for not just service but also sales in banking. For instance, pre-approving a customer for a loan via chat and guiding them through acceptance, all within a minute or two.
In fact, an older prediction stated that by 2025, AI would drive 95% of customer interactions, including sales and support. We're seeing that trajectory now.
How Regulations Will Shape Banking AI Development
Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing AI, especially in finance. We can expect guidelines or rules around transparency (e.g., requiring banks to disclose when an AI is interacting with a customer), fairness (ensuring AI doesn't inadvertently discriminate or deny service unfairly), and auditability (banks may need to explain an AI decision, like why a loan via AI was denied, in human-understandable terms).
Banks will likely err on the side of caution and incorporate things like AI "ethics checks" and more rigorous testing before releasing new AI features. The ones that navigate this well will gain public trust. It's possible that in a few years, having a well-regarded AI assistant could be seen as a mark of a forward-thinking but responsible bank.
In short, the future of AI in banking customer service looks bright: more natural interactions, more ubiquitous presence, and even greater efficiency. But it'll remain essential to keep the human element in focus. Virtually all experts agree that AI won't replace humans in customer service. Instead it'll handle the heavy lifting so humans can deliver higher-touch service when it counts.
Banks that strike this balance will likely see the best of both worlds: happy customers and efficient operations.
How to Implement AI in Your Bank's Customer Service: Step-by-Step Checklist
If you're part of a financial institution looking to deploy AI in customer service (or enhance what you have), here's a condensed checklist of steps and considerations to guide a successful setup:
Step 1: Find Where AI Will Help Your Bank Most
Start by pinpointing where AI can add the most value for your bank. Look at your support data. What are the most common questions or tasks that eat up agent time? Those are prime candidates for automation. It might be simple account inquiries, password resets, or FAQs.
Also consider processes customers find tedious (like filling forms, waiting for updates). Prioritize use cases by potential impact (cost savings, volume, improvement to CX) and feasibility.
Step 2: Choose Your AI Banking Platform
Decide whether to build in-house, use a platform, or a hybrid. There are many AI chatbot providers, but few are tailored to banking needs (security, compliance, etc.).
Key features to look for include:
-
Robust NLP capabilities
-
Easy integration tools (APIs or connectors for your core systems)
-
Support for multiple channels (web, mobile, messaging apps)
-
Built-in security/compliance measures
For instance, Social Intents is a platform known for its codeless AI chatbots, which means you can launch a fully functional chatbot without a heavy development project. This can speed up deployment, especially if your team lacks AI engineers.
The solution you choose should also allow a multichannel presence. Social Intents works across websites, mobile apps, and even works with messaging platforms like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger for real-time support wherever your customers are.
A good platform will also support easy updates (so your business users can tweak bot replies or add FAQs without coding) and analytics to monitor performance.
Step 3: Get Security and Compliance Right from Day One
Engage your IT security and compliance departments early. Make sure any data the AI accesses or stores is encrypted and handled according to your policies. Set rules for data retention (e.g. chat logs) in line with privacy laws.
If using third-party AI providers, scrutinize their security certifications and consider where the data is hosted (some banks require on-premise or private cloud deployments for sensitive data).
Also, set the bot to authenticate users properly before revealing account info. Many solutions allow integration with your existing login or identity verification process.
Lastly, have a plan for regulatory compliance. For example, if the AI gives any kind of financial "advice", ensure disclaimers are provided. If it's involved in lending decisions, be mindful of fair lending regulations.
Step 4: Connect Your AI to Banking Systems and Test Everything
Work with your IT team to hook the chatbot into necessary systems. This could mean API development so the AI can do things like check balances, execute transfers, or pull up transaction histories.
Once built, test thoroughly. Use real-world scenarios and data in a sandbox to see if the AI responds correctly. Involve some of your actual call center agents in testing. They can throw common customer questions at it and see if it holds up or where it fails.
Also test edge cases (typos, slang, code-mixed languages like "Spanglish", etc.) to ensure the NLP is robust. At this phase, also craft the conversational flows: how should the bot introduce itself? How does it guide users for multi-step tasks? Write responses that fit your brand's tone (professional yet friendly, for example).
Testing should also include the escalation path to human agents. Simulate a handoff and see if the agent gets all the info context. It's wise to soft-launch internally or with a small user group first, to catch any issues.
Step 5: Prepare Your Team for AI-Human Collaboration
Prepare your customer service team for the AI assistant. Make sure agents know what the bot will handle, and how the escalation works on their side (e.g., will they see a summary of the bot conversation?).
Train them to work with the AI. For instance, if the bot hands off a customer, the agent should read the context first rather than asking the customer to repeat.
Some staff may worry about AI. Reassure them that it's there to help, not replace, and perhaps create new roles like "bot manager" or "AI trainer" that experienced agents can move into.
Adjust your workflow to incorporate AI. For example, if the bot handles 50% of Tier-1 chats, you might repurpose some frontline agents to be "overflow" or to focus on upselling and relationship-building with customers who do come through human channels.
Also decide how you'll measure the bot's performance and define success (is it containment rate? CSAT? Reduction in email inquiries?). Set those KPIs up front.
Step 6: Launch Your Banking AI (Start Small, Scale Smart)
When rolling out the bot to customers, do it in phases if possible. Perhaps start with chat on the website for a subset of customers or in a beta mode. Monitor the interactions closely. Collect feedback. Many banks have the bot ask at the end "Was this helpful? Yes/No" or have a quick survey.
Use that feedback to iron out kinks. Once you're confident, promote the AI assistant. Introduce it via email newsletters, on your login portal, on social media. Highlight the convenience: "Now you can get help 24/7 with our new virtual assistant." Provide examples of things it can do ("Ask about transactions, get instant answers to FAQs, and more").
The more customers know about it, the faster they'll try it. Also, consider giving it a friendly name and identity, something that aligns with your brand. This isn't just a gimmick. It actually helps customers form a mental model ("Oh, I can ask [name] and it'll help me"). People are surprisingly open to anthropomorphized AI when it's helpful and polite.
Make sure to disclose it's an AI (most banks do this anyway for transparency).
Step 7: Keep Improving Your Banking AI
After launch, set up a team or at least a point person to review how things are going. Use the analytics from the chatbot platform: look at containment rate (what percent of chats the bot solved vs. escalated), which questions are most asked (and ensure the answers to those are spot-on), where the bot fails or confuses users (and then improve those dialogues).
Maintain a living knowledge base. As new customer issues arise (e.g., a new type of scam, a new product), update the bot so it can handle them. Keep training the NLP model with real chat logs (while respecting privacy; typically this is aggregated data).
Also, keep your content up to date. If fees change or policies update, ensure the bot's answers update too (this can be managed similarly to how you update your website FAQs or internal knowledge base).
Essentially, treat the AI assistant as a developing digital employee: it needs ongoing coaching and information to perform well.
Regularly get feedback from your human agents about the quality of leads or escalations they get from the bot. Are they useful, or is the bot handing off too early/late? Tweak the confidence thresholds accordingly.
Also, stay tuned to user sentiment. If customers start complaining, address it quickly. Conversely, track positive outcomes like reduced call volumes, higher self-service usage, or improved customer survey scores after doing the bot, to quantify the ROI of the project.
Step 8: Expand Your AI Capabilities Over Time
Once the chatbot handles the initial scope well, you can consider expanding its capabilities. For example, if it started with retail banking questions, perhaps extend it to credit card-specific help, or small business banking queries, etc.
Eventually it might even handle cross-selling ("Would you like to learn about our mortgage rates?" if relevant in a convo). Working AI with more systems can unlock new use cases. For instance, linking to your CRM could let the bot inform a customer "your financial advisor is out this week, can I schedule you with another?"
The possibilities grow as the AI proves itself. Also consider adding voice if you launched with text, or vice versa, to unify the service across channels. And as more advanced AI tech (like new NLP models) becomes stable, evaluate if an upgrade could make the bot even better.
Many banks are on their 2nd or 3rd generation of chatbots now, constantly changing them as technology and customer expectations advance.
Common Questions About AI in Banking Customer Service
How long does it take to set up AI customer service in a bank?
The timeline varies significantly based on your approach. If you build a custom solution from scratch, expect 6-12 months or longer for development, integration, testing, and regulatory approval. But using a modern platform like Social Intents can reduce this to just 3-5 days for basic setup.
Most banks start with a pilot focused on specific use cases (like FAQs or account inquiries), prove ROI in 30-60 days, and then gradually expand capabilities. This phased approach reduces risk and allows you to learn what works before full-scale deployment.
The key factors affecting timeline are: complexity of system integrations, scope of initial use cases, internal approval processes, and whether you're building custom or using an existing platform. Social Intents' no-code approach means you can be operational in days, not months.
Is AI customer service secure enough for banking?
Security is non-negotiable in banking, and modern AI platforms are built with this in mind. When properly done, AI customer service can be extremely secure. Look for platforms that offer end-to-end encryption, secure API integrations, audit logs, role-based access controls, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Social Intents was built with enterprise-grade security features specifically for industries like banking that handle sensitive customer data. The platform encrypts all communications, works with your existing authentication systems, and provides the audit trails necessary for regulatory compliance.
The key is choosing a vendor with a proven track record in financial services and ensuring your setup follows security best practices. Your IT security team should be involved from day one to validate the approach.
Will AI replace our human customer service agents?
No. The goal of AI in banking customer service is to augment human agents, not replace them. AI excels at handling high-volume, repetitive tasks (like checking balances, resetting passwords, answering FAQs), which frees up your human agents to focus on complex issues that require empathy, judgment, and problem-solving.
Research shows that customers still prefer humans for complex or sensitive matters. The most successful setups use AI to handle tier-1 inquiries while routing more complex issues to skilled human agents. This hybrid model actually improves both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Many banks report that AI has made their agents more effective and engaged by removing the tedious parts of their job, allowing them to focus on higher-value interactions where they can make a real difference for customers.
How much does it cost to set up AI customer service?
Costs vary dramatically depending on your approach. Building a custom AI solution from scratch can cost hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars in development, integration, and ongoing maintenance.
Platform-based solutions like Social Intents are far more cost-effective, with plans starting at $39/month and scaling based on your needs. Most banks find that even modest AI setups deliver ROI within 3-6 months through reduced call center costs and improved efficiency.
Remember that a chatbot interaction costs around $0.50 versus $6.00 for a human agent. If your AI handles even 100 inquiries per day, that's $500 in daily savings ($182,500 annually). The platform cost is typically recovered many times over through operational savings.
Social Intents offers a 14-day free trial so you can test the platform and calculate your specific ROI before committing.
How do we handle integration with our existing banking systems?
Integration is crucial for delivering valuable AI customer service. Your chatbot needs access to core banking systems (for balances, transactions), CRM (for customer data), payment systems, and other relevant databases.
Modern platforms like Social Intents provide secure API capabilities that allow you to connect the chatbot to your existing systems. The platform's Custom AI Actions feature enables you to create custom integrations with your third-party tools and banking systems, allowing the chatbot to retrieve real-time data and execute actions.
Your IT team will typically create secure APIs that the chatbot can call (with proper authentication and authorization). Most banks start with read-only integrations (checking balances, showing transactions) and gradually add transactional capabilities (transfers, payments) as confidence grows.
The integration work is significantly simpler when using a platform versus building from scratch, because the platform handles the chatbot infrastructure and you just need to create the specific connectors to your systems.
What if customers get frustrated with the AI?
This is a valid concern, and it's why seamless human escalation is so important. The best practice is to never trap customers in an AI-only experience. Customers should always have an easy path to reach a human agent when needed.
Social Intents excels at this with its seamless human escalation feature. The AI can automatically detect frustration (through keywords like "agent", "representative", or sentiment analysis) and immediately transfer the conversation to a human agent, along with the full conversation history.
This approach gives customers confidence that they can get human help whenever they need it, which actually increases their willingness to try the AI first. Most customers appreciate getting instant AI help for simple questions, knowing that complex issues will be handled by a person.
The key is setting clear expectations up front about what the AI can and can't do, and making the escalation process completely frictionless.
How do we measure the success of our AI customer service?
Success metrics should align with your goals. Common KPIs include:
Containment rate: Percentage of inquiries resolved by AI without human escalation (target: 70-80% for routine inquiries)
Customer satisfaction (CSAT): Rating given after AI interactions (target: 80%+ positive)
Average handling time: Time to resolution for AI vs. human interactions
Cost per interaction: AI ($0.50) vs. human ($6.00)
Call center volume reduction: Decrease in phone calls and emails after AI deployment
First contact resolution: Percentage of issues resolved in first interaction
Agent productivity: Time saved by agents due to AI handling routine tasks
Social Intents provides built-in analytics to track these metrics, allowing you to show ROI and identify areas for improvement. Most banks see measurable improvements within 30-60 days of deployment.
Why choose Social Intents over other AI chatbot platforms?
Social Intents was specifically designed to address the common pain points banks face with AI customer service:
Speed to deployment: No-code setup means you're live in days, not months. Build custom in months? Or deploy Social Intents this week?
Native tool integration: Your agents respond from Teams, Slack, Google Chat, Zoom, or Webex. No new tool to learn.
Seamless human handoff: AI automatically escalates to humans with full context when needed. No frustrated customers stuck in bot loops.
Unlimited agents: From Basic plans up, add as many agents as you need without per-agent fees.
Custom AI Actions: Work with your banking systems for real transactional capabilities, not just information retrieval.
Multichannel support: Deploy once, reach customers on web, mobile, WhatsApp, Messenger, and more.
Enterprise security: Built for regulated industries with encryption, compliance, and audit capabilities.
Proven in financial services: Used by banks, credit unions, and fintech companies who needed results fast.
The combination of ease of use, speed of deployment, and enterprise capabilities makes Social Intents ideal for banks that want AI customer service without the complexity and cost of custom development.
Final Thoughts

AI in banking customer service is no longer a futuristic concept. It's here, delivering tangible benefits for institutions that do it thoughtfully. Banks adopting AI are seeing faster customer service, lower costs, and new ways to engage and delight their customers.
From answering basic questions in seconds, to safeguarding accounts with instant fraud alerts, to guiding users through complex tasks step by step, AI is helping banks provide a level of service that would've been hard to imagine just a decade ago. And importantly, it's doing so in a way that lets human employees focus on what they do best: understanding nuanced customer needs, building relationships, and solving unique problems.
That said, success with AI requires careful planning and execution. The technology is powerful, but it must be applied thoughtfully, with robust training, integration, and a customer-first mindset. Banks that rush in with a poorly designed bot risk irritating customers or creating security gaps. But those that get it right are setting a new standard for convenience and service quality.
They're showing that banking can be as easy as texting your very own financial assistant, any time, anywhere.
Looking ahead, as AI continues to change, we can expect the gap between digital and in-person service to narrow further. Virtually 100% of customer interactions may involve some form of AI support in the near future, whether customers realize it or not. But the human element will remain critical. The most successful banks will be those that combine AI efficiency with human empathy in a seamless way.
In doing so, they won't only cut costs or handle volume. They'll actually improve the quality of customer experience, making banking feel more personalized and proactive.
For any bank leader or customer service professional reading this: the time to start (or speed up) your AI journey is now. The tools are mature, and customers are increasingly expecting intelligent self-service options. With a solid strategy and the right partners, doing AI in your banking customer service can be a game-changing move, one that pays dividends in customer satisfaction, loyalty, and operational excellence.
Ready to transform your bank's customer service with AI? Visit Social Intents today to start your free 14-day trial and see how quickly you can deliver AI-powered support that your customers will love and your team will appreciate.


